Page 239 - Intro Predictive Maintenance
P. 239
230 An Introduction to Predictive Maintenance
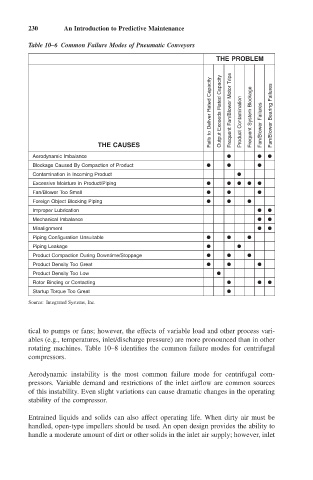
Table 10–6 Common Failure Modes of Pneumatic Conveyors
THE PROBLEM
Fails to Deliver Rated Capacity Output Exceeds Rated Capacity Frequent Fan/Blower Motor Trips Product Contamination Frequent System Blockage Fan/Blower Failures Fan/Blower Bearing Failures
THE CAUSES
Aerodynamic Imbalance
Blockage Caused By Compaction of Product
Contamination in Incoming Product
Excessive Moisture in Product/Piping
Fan/Blower Too Small
Foreign Object Blocking Piping
Improper Lubrication
Mechanical Imbalance
Misalignment
Piping Configuration Unsuitable
Piping Leakage
Product Compaction During Downtime/Stoppage
Product Density Too Great
Product Density Too Low
Rotor Binding or Contacting
Startup Torque Too Great
Source: Integrated Systems, Inc.
tical to pumps or fans; however, the effects of variable load and other process vari-
ables (e.g., temperatures, inlet/discharge pressure) are more pronounced than in other
rotating machines. Table 10–8 identifies the common failure modes for centrifugal
compressors.
Aerodynamic instability is the most common failure mode for centrifugal com-
pressors. Variable demand and restrictions of the inlet airflow are common sources
of this instability. Even slight variations can cause dramatic changes in the operating
stability of the compressor.
Entrained liquids and solids can also affect operating life. When dirty air must be
handled, open-type impellers should be used. An open design provides the ability to
handle a moderate amount of dirt or other solids in the inlet air supply; however, inlet