Page 347 - Introduction to AI Robotics
P. 347
330
landmark 1 9 Topological Path Planning
landmark 4
landmark 2
landmark 3
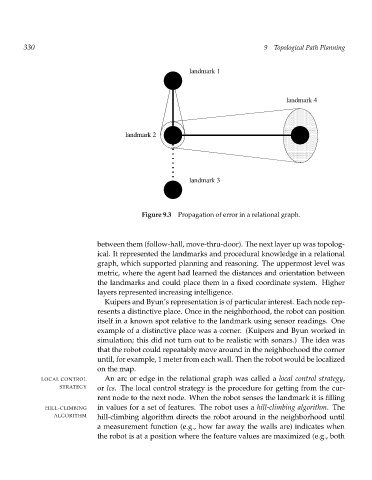
Figure 9.3 Propagation of error in a relational graph.
between them (follow-hall, move-thru-door). The next layer up was topolog-
ical. It represented the landmarks and procedural knowledge in a relational
graph, which supported planning and reasoning. The uppermost level was
metric, where the agent had learned the distances and orientation between
the landmarks and could place them in a fixed coordinate system. Higher
layers represented increasing intelligence.
Kuipers and Byun’s representation is of particular interest. Each node rep-
resents a distinctive place. Once in the neighborhood, the robot can position
itself in a known spot relative to the landmark using sensor readings. One
example of a distinctive place was a corner. (Kuipers and Byun worked in
simulation; this did not turn out to be realistic with sonars.) The idea was
that the robot could repeatably move around in the neighborhood the corner
until, for example, 1 meter from each wall. Then the robot would be localized
on the map.
LOCAL CONTROL An arc or edge in the relational graph was called a local control strategy,
STRATEGY or lcs. The local control strategy is the procedure for getting from the cur-
rent node to the next node. When the robot senses the landmark it is filling
HILL-CLIMBING in values for a set of features. The robot uses a hill-climbing algorithm.The
ALGORITHM hill-climbing algorithm directs the robot around in the neighborhood until
a measurement function (e.g., how far away the walls are) indicates when
the robot is at a position where the feature values are maximized (e.g., both