Page 348 - Introduction to AI Robotics
P. 348
9.3 Relational Methods
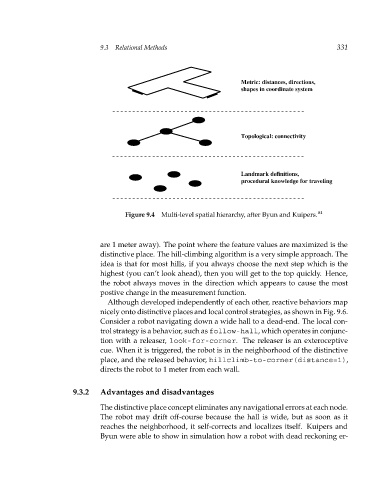
Metric: distances, directions, 331
shapes in coordinate system
Topological: connectivity
Landmark definitions,
procedural knowledge for traveling
Figure 9.4 Multi-level spatial hierarchy, after Byun and Kuipers. 81
are 1 meter away). The point where the feature values are maximized is the
distinctive place. The hill-climbing algorithm is a very simple approach. The
idea is that for most hills, if you always choose the next step which is the
highest (you can’t look ahead), then you will get to the top quickly. Hence,
the robot always moves in the direction which appears to cause the most
postive change in the measurement function.
Although developed independently of each other, reactive behaviors map
nicely onto distinctive places and local control strategies, as shown in Fig. 9.6.
Consider a robot navigating down a wide hall to a dead-end. The local con-
trol strategy is a behavior, such as follow-hall, which operates in conjunc-
tion with a releaser, look-for-corner. The releaser is an exteroceptive
cue. When it is triggered, the robot is in the neighborhood of the distinctive
place, and the released behavior, hillclimb-to-corner(distance=1),
directs the robot to 1 meter from each wall.
9.3.2 Advantages and disadvantages
The distinctive place concept eliminates any navigational errors at each node.
The robot may drift off-course because the hall is wide, but as soon as it
reaches the neighborhood, it self-corrects and localizes itself. Kuipers and
Byun were able to show in simulation how a robot with dead reckoning er-