Page 422 - Introduction to AI Robotics
P. 422
11.6 Comparison of Methods
[0][0] 405
Sonar model parameters:
R=10
tolerance =+/- 0.5
Max_occupied = 0.98
β=15
t2 t3
t1
[23][20]
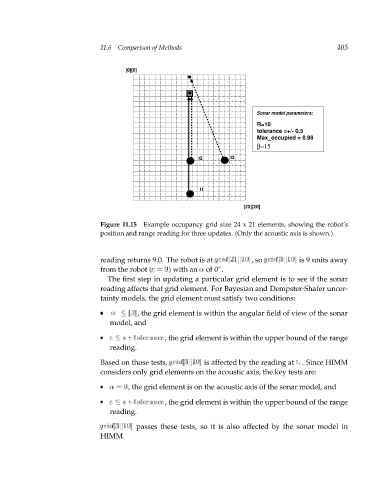
Figure 11.15 Example occupancy grid size 24 x 21 elements, showing the robot’s
position and range reading for three updates. (Only the acoustic axis is shown.)
reading returns 9.0. The robot is at g r[21][10] i d ,so g r[3][10] i d is 9 units away
from the robot (r = )withan of 0 . 9
The first step in updating a particular grid element is to see if the sonar
reading affects that grid element. For Bayesian and Dempster-Shafer uncer-
tainty models, the grid element must satisfy two conditions:
j j j, the grid lement is within the angular field of view of the sonar
j
e
model, and
r s + tolerance , the grid element is within the upper bound of the range
reading.
Based on those tests, g r[3][10] i d is affected by the reading at t 1 .Since HIMM
considers only grid elements on the acoustic axis, the key tests are:
= , the grid element is on the acoustic axis of the sonar model, and
0
r s + tolerance , the grid element is within the upper bound of the range
reading.
g r[3][10] i d passes these tests, so it is also affected by the sonar model in
HIMM.