Page 208 - Introduction to Autonomous Mobile Robots
P. 208
Mobile Robot Localization
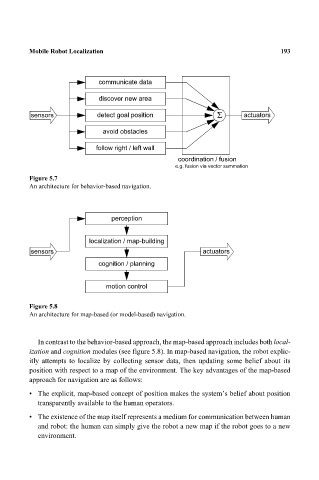
communicate data 193
discover new area
sensors detect goal position Σ actuators
avoid obstacles
follow right / left wall
coordination / fusion
e.g. fusion via vector summation
Figure 5.7
An architecture for behavior-based navigation.
perception
localization / map-building
sensors actuators
cognition / planning
motion control
Figure 5.8
An architecture for map-based (or model-based) navigation.
In contrast to the behavior-based approach, the map-based approach includes both local-
ization and cognition modules (see figure 5.8). In map-based navigation, the robot explic-
itly attempts to localize by collecting sensor data, then updating some belief about its
position with respect to a map of the environment. The key advantages of the map-based
approach for navigation are as follows:
• The explicit, map-based concept of position makes the system’s belief about position
transparently available to the human operators.
• The existence of the map itself represents a medium for communication between human
and robot: the human can simply give the robot a new map if the robot goes to a new
environment.