Page 288 - Introduction to Autonomous Mobile Robots
P. 288
Planning and Navigation
goal 273
L2
H1 L1 H2
start
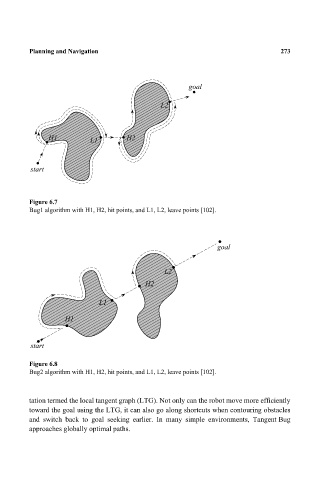
Figure 6.7
Bug1 algorithm with H1, H2, hit points, and L1, L2, leave points [102].
goal
L2
H2
L1
H1
start
Figure 6.8
Bug2 algorithm with H1, H2, hit points, and L1, L2, leave points [102].
tation termed the local tangent graph (LTG). Not only can the robot move more efficiently
toward the goal using the LTG, it can also go along shortcuts when contouring obstacles
and switch back to goal seeking earlier. In many simple environments, Tangent Bug
approaches globally optimal paths.