Page 304 - Introduction to Autonomous Mobile Robots
P. 304
Planning and Navigation
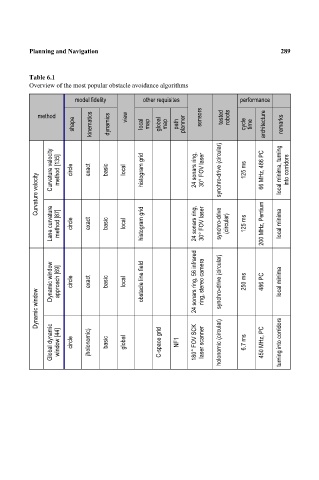
Table 6.1 289
Overview of the most popular obstacle avoidance algorithms
model fidelity other requisites performance
method view sensors tested robots
shape kinematics dynamics local map global map path planner cycle time architecture remarks
Curvature velocity method [135] circle exact basic local histogram grid 24 sonars ring, 30° FOV laser synchro-drive (circular) 125 ms 66 MHz, 486 PC local minima, turning into corridors
Curvature velocity
Lane curvature method [87] circle exact basic local histogram grid 24 sonars ring, 30° FOV laser synchro-drive (circular) 125 ms 200 MHz, Pentium local minima
Dynamic window approach [69] circle exact basic local obstacle line field 24 sonars ring, 56 infrared ring, stereo camera synchro-drive (circular) 250 ms 486 PC local minima
Dynamic window
Global dynamic window [44] circle (holonomic) basic global C-space grid NF1 180° FOV SCK laser scanner holonomic (circular) 6.7 ms 450 MHz, PC turning into corridors