Page 305 - Introduction to Autonomous Mobile Robots
P. 305
290
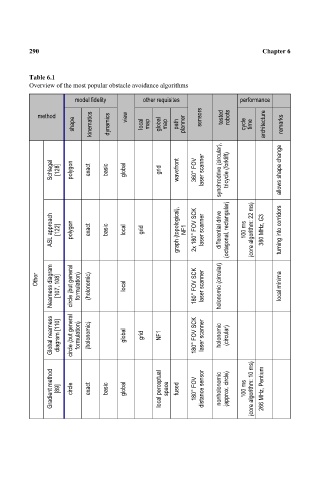
Table 6.1 Chapter 6
Overview of the most popular obstacle avoidance algorithms
model fidelity other requisites performance
method view sensors tested robots
shape kinematics dynamics local map global map path planner cycle time architecture remarks
Schlegel [128] polygon exact basic global grid wavefront 360° FOV laser scanner synchrodrive (circular), tricycle (forklift) allows shape change
ASL approach [122] polygon exact basic local grid graph (topological), NF1 2x 180° FOV SCK laser scanner differential drive (octagonal, rectangular) 100 ms (core algorithm: 22 ms) 380 MHz, G3 turning into corridors
Nearness diagram [107, 108] circle (but general formulation) (holonomic) local 180° FOV SCK laser scanner holonomic (circular) local minima
Other
Global nearness diagram [110] circle (but general formulation) (holonomic) global grid NF1 180° FOV SCK laser scanner holonomic (circular)
Gradient method [89] circle exact basic global local perceptual space fused 180° FOV distance sensor nonholonomic (approx. circle) 100 ms (core algorithm: 10 ms) 266 MHz, Pentium