Page 35 - Introduction to Autonomous Mobile Robots
P. 35
20
free fly Chapter 2
changeover walking galloping
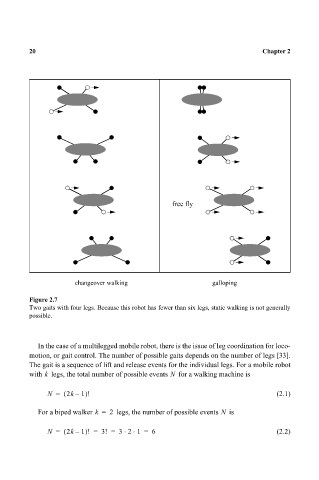
Figure 2.7
Two gaits with four legs. Because this robot has fewer than six legs, static walking is not generally
possible.
In the case of a multilegged mobile robot, there is the issue of leg coordination for loco-
motion, or gait control. The number of possible gaits depends on the number of legs [33].
The gait is a sequence of lift and release events for the individual legs. For a mobile robot
N
with legs, the total number of possible events for a walking machine is
k
N = ( 2k – 1)! (2.1)
N
For a biped walker k = 2 legs, the number of possible events is
⋅
⋅
N = ( 2k – 1)! = 3! = 3 2 1 = 6 (2.2)