Page 231 - Introduction to Colloid and Surface Chemistry
P. 231
220 Colloid stability
Distance between particles (H)
/ V A
/
/
/
/
/
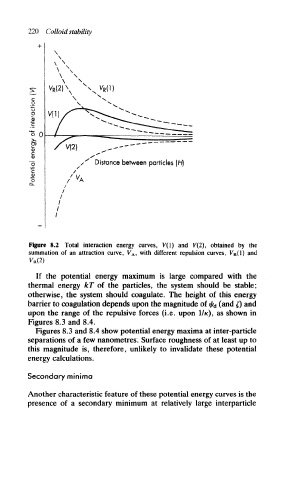
Figure 8.2 Total interaction energy curves, V(l) and V(2), obtained by the
summation of an attraction curve, V A, with different repulsion curves, V R(1) and
If the potential energy maximum is large compared with the
thermal energy kT of the particles, the system should be stable;
otherwise, the system should coagulate. The height of this energy
barrier to coagulation depends upon the magnitude of </r d (and £) and
upon the range of the repulsive forces (i.e. upon I/K), as shown in
Figures 8.3 and 8.4.
Figures 8.3 and 8.4 show potential energy maxima at inter-particle
separations of a few nanometres. Surface roughness of at least up to
this magnitude is, therefore, unlikely to invalidate these potential
energy calculations.
Secondary minima
Another characteristic feature of these potential energy curves is the
presence of a secondary minimum at relatively large interparticle