Page 233 - Introduction to Colloid and Surface Chemistry
P. 233
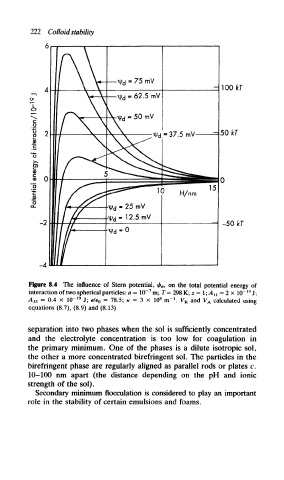
222 Colloid stability
6
- }QOkT
5QkT
-50 kT
Figure 8.4 The influence of Stern potential, ifa, on the total potential energy of
7
19
interaction of two spherical particles: a = 10" m; T = 298 K; z - 1; A „ = 2 x 10" J;
1
19
8
= 0.4 x 1(T J; = 78.5; K = 3 x 10 nr . and calculated using
A 33 e/e 0 V R V A
equations (8.7), (8.9) and (8.13)
separation into two phases when the sol is sufficiently concentrated
and the electrolyte concentration is too low for coagulation in
the primary minimum. One of the phases is a dilute isotropic sol,
the other a more concentrated birefringent sol. The particles in the
birefringent phase are regularly aligned as parallel rods or plates c.
10-100 nm apart (the distance depending on the pH and ionic
strength of the sol).
Secondary minimum flocculation is considered to play an important
role in the stability of certain emulsions and foams.