Page 202 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 202
3.3. Critical Components
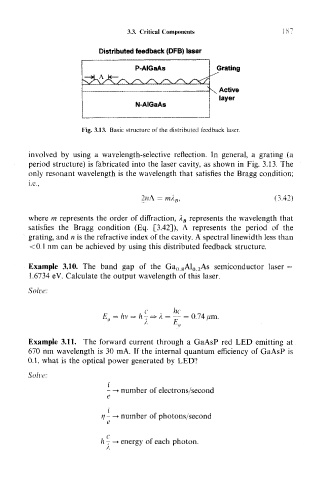
Distributed feedback (DFB) laser
P-AIGaAs Grating
s Active
layer
N-AIGaAs
Fig. 3.13. Basic structure of the distributed feedback laser.
involved by using a wavelength-selective reflection. In general, a grating (a
period structure) is fabricated into the laser cavity, as shown in Fig. 3.13. The
only resonant wavelength is the wavelength that satisfies the Bragg condition;
i.e.,
2?zA = mA (3.42)
where m represents the order of diffraction, A B represents the wavelength that
satisfies the Bragg condition (Eq. [3.42]), A represents the period of the
grating, and n is the refractive index of the cavity. A spectral linewidth less than
<0.1 nm can be achieved by using this distributed feedback structure.
Example 3.10. The band gap of the Ga 0 8A1 0 2As semiconductor laser =
1.6734 eV. Calculate the output wavelength of this laser.
Solve:
, c . he
= nv = /i - => / = — — 0.74 /urn.
A £,,
Example 3.11. The forward current through a GaAsP red LED emitting at
670 nm wavelength is 30 mA. If the internal quantum efficiency of GaAsP is
0.1, what is the optical power generated by LED?
Solve:
—>• number of electrons/second
v\ —> number of photons/second
e
h - —>• energy of each photon.