Page 205 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 205
190 3. Communication with Optics
Multiplication
e-h creation region
-AAAAA--*•
P P n u
electron
<i
/ < >
V T
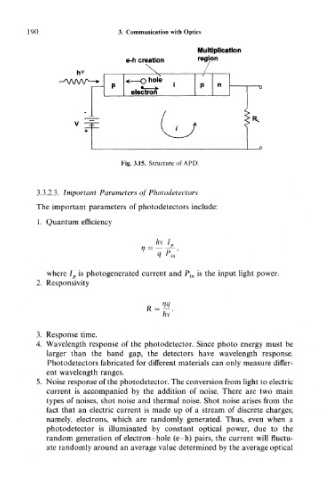
Fig. 3.15. Structure of APD.
3.3.2,3. Important Parameters of Photodetectors
The important parameters of photodetectors include:
1. Quantum efficiency
where I p is photogenerated current and P in is the input light power.
2. Responsivity
D __
hv
3. Response time.
4. Wavelength response of the photodetector. Since photo energy must be
larger than the band gap, the detectors have wavelength response.
Photodetectors fabricated for different materials can only measure differ-
ent wavelength ranges.
5. Noise response of the photodetector. The conversion from light to electric
current is accompanied by the addition of noise. There are two main
types of noises, shot noise and thermal noise. Shot noise arises from the
fact that an electric current is made up of a stream of discrete charges;
namely, electrons, which are randomly generated. Thus, even when a
photodetector is illuminated by constant optical power, due to the
random generation of electron-hole (e-h) pairs, the current will fluctu-
ate randomly around an average value determined by the average optical