Page 235 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 235
220 4. Switching with Optics
substrate materials include glass, semiconductors (both GaAs and InP), and
LiNbO 3.
In this section we consider thin film and waveguide modulators based on
the electro-optic effect. The main characteristics and the performance of
LiNbO 3 and semiconductor devices will be discussed. The materials presented
here are based on several publications [8,14,15,16].
4.3.1. DIRECT MODULATION OF SEMICONDUCTOR LASERS
Direct modulation of diode lasers offers a simple approach to the generation
of coded optical pulses [17]. In this case, an external electrical signal modulates
the gain in the medium. Since the minimum loss in conventional silica fibers
occurs at around 1.55 /mi wavelength and the zero-dispersion wavelength is
near 1.3 /mi, semiconductor laser sources, which have small size and matched
wavelengths, have attracted attention as the most promising candidates for
application in this field. Another advantage of diode lasers over other types of
lasers is that the optical signal can be directly modulated by the drive current.
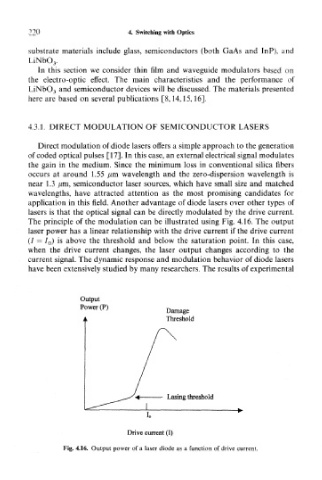
The principle of the modulation can be illustrated using Fig. 4.16. The output
laser power has a linear relationship with the drive current if the drive current
(/ = IQ) is above the threshold and below the saturation point. In this case,
when the drive current changes, the laser output changes according to the
current signal. The dynamic response and modulation behavior of diode lasers
have been extensively studied by many researchers. The results of experimental
Output
Power (P)
Damage
Threshold
Drive current (I)
Fig. 4.16. Output power of a laser diode as a function of drive current.