Page 237 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 237
222 4. Switching with Optics
obtained by a small-signal analysis of the rate equations. The small-signal
response of the intrinsic laser is obtained by linearizing laser rate equations and
can be found [19] as
(4,28)
2
2
X
' '~(co -a>g) +a>y'
where y is the damping rate, and to 0 is the resonance frequency is given by
9 o s
(4.29)
where g 0 is the small gain coefficient, S is the steady-state photon density, and
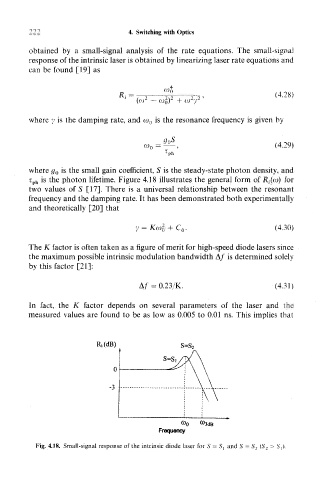
t ph is the photon lifetime. Figure 4.18 illustrates the general form of JR,-(o>) for
two values of S [17]. There is a universal relationship between the resonant
frequency and the damping rate. It has been demonstrated both experimentally
and theoretically [20] that
(4.30)
The K factor is often taken as a figure of merit for high-speed diode lasers since
the maximum possible intrinsic modulation bandwidth A/ is determined solely
by this factor [21]:
A/ = 0.23/K. (4.31)
In fact, the K factor depends on several parameters of the laser and the
measured values are found to be as low as 0.005 to 0.01 ns. This implies that
Ri(dB)
S=S 2
C0 0
Frequency
Fig. 4.18. Small-signal response of the intrinsic diode laser for S = S, and S = S 2 (S 2 > S,