Page 319 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 319
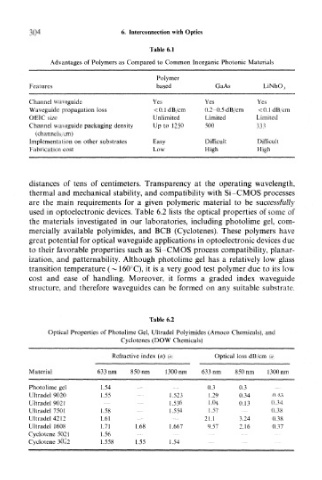
304 6. Interconnection with Optics
Table 6.1
Advantages of Polymers as Compared to Common Inorganic Photonic Materials
Polymer
Features based GaAs LiNbO,,
Channel waveguide Yes Yes Yes
Waveguide propagation loss <0.1dB/cm 0.2-0.5 dB/cm < 0.1 dB/cm
OEIC size Unlimited Limited Limited
Channel waveguide packaging density Up to 1250 500 333
(channels/cm)
Implementation on other substrates Easy Difficult Difficult
Fabrication cost Low High High
distances of tens of centimeters. Transparency at the operating wavelength,
thermal and mechanical stability, and compatibility with Si-CMOS processes
are the main requirements for a given polymeric material to be successfully
used in optoelectronic devices. Table 6.2 lists the optical properties of some of
the materials investigated in our laboratories, including photolime gel, com-
mercially available polyimides, and BCB (Cyclotenes). These polymers have
great potential for optical waveguide applications in optoelectronic devices due
to their favorable properties such as Si-CMOS process compatibility, planar-
ization, and patternability. Although photolime gel has a relatively low glass
transition temperature (~ 160°C), it is a very good test polymer due to its low
cost and ease of handling. Moreover, it forms a graded index waveguide
structure, and therefore waveguides can be formed on any suitable substrate.
Table 6.2
Optical Properties of Photolime Gel, Ultradel Polyimides (Amoco Chemicals), and
Cyclotenes (DOW Chemicals)
Refractive index («) (« Optical loss dB/cm (a.
Material 633 nm 850 nm IJOOnm 633 nm 850 nm UOOnm
Photolime gel 1.54 0.3 0.3
Ultradel 9020 1.55 1.523 1.29 0.34 0.43
Ultradel 9021 1.536 1.04 0.13 0.34
Ultradel 7501 1.58 1.554 1.57 0.38
Ultradel 4212 1.61 21.1 3.24 0.38
Ultradel 1608 1.71 1.68 1.667 9.57 2.16 0.37
Cyclotene502I 1.56
Cyclotene 3022 1.558 1.55 1.54