Page 405 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 405
390 7. Pattern Recognition with Optics
16
14 - -•— With anti-target in training
-O • without anti-target in training
•5
CO
Q.
03 10
O
0
Q 8 -
C
(0
Q) O-
Q_
2 -
1 32x32 64x64 128x128
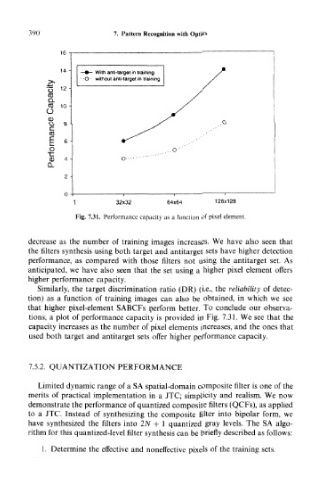
Fig. 7.31. Performance capacity as a function of pixel element.
decrease as the number of training images increases. We have also seen that
the filters synthesis using both target and antitarget sets have higher detection
performance, as compared with those filters not using the antitarget set. As
anticipated, we have also seen that the set using a higher pixel element offers
higher performance capacity.
Similarly, the target discrimination ratio (DR) (i.e., the reliability of detec-
tion) as a function of training images can also be obtained, in which we see
that higher pixel-element SABCFs perform better. To conclude our observa-
tions, a plot of performance capacity is provided in Fig. 7.31. We see that the
capacity increases as the number of pixel elements increases, and the ones that
used both target and antitarget sets offer higher performance capacity.
7.5.2. QUANTIZATION PERFORMANCE
Limited dynamic range of a SA spatial-domain composite filter is one of the
merits of practical implementation in a JTC; simplicity and realism. We now
demonstrate the performance of quantized composite filters (QCFs), as applied
to a JTC. Instead of synthesizing the composite filter into bipolar form, we
have synthesized the filters into 2JV + 1 quantized gray levels. The SA algo-
rithm for this quantized-level filter synthesis can be briefly described as follows:
Determine the effective and noneffective pixels of the training sets.