Page 410 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 410
7.6. Pattern Classification 39:
•1 2-1
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
Noise Standard Deviation 8
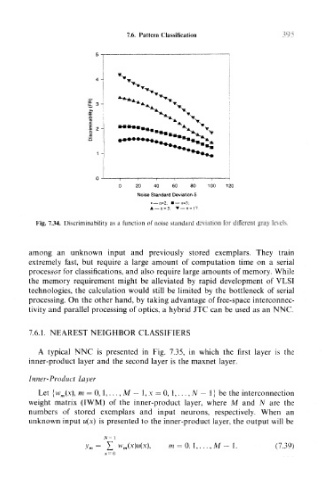
Fig. 7.34. Discriminability as a function of noise standard deviation for different gray levels.
among an unknown input and previously stored exemplars. They train
extremely fast, but require a large amount of computation time on a serial
processor for classifications, and also require large amounts of memory. While
the memory requirement might be alleviated by rapid development of VLSI
technologies, the calculation would still be limited by the bottleneck of serial
processing. On the other hand, by taking advantage of free-space interconnec-
tivity and parallel processing of optics, a hybrid JTC can be used as an NNC.
7.6.1. NEAREST NEIGHBOR CLASSIFIERS
A typical NNC is presented in Fig. 7.35, in which the first layer is the
inner-product layer and the second layer is the maxnet layer.
Inner-Product Layer
Let |w m(x), m = 0,1,..., M -- 1, x — 0, 1,..., N — 1 }• be the interconnection
weight matrix (IWM) of the inner-product layer, where M and JV are the
numbers of stored exemplars and input neurons, respectively. When an
unknown input u(x) is presented to the inner-product layer, the output will be
= Z (7.39)