Page 411 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 411
396 7. Pattern Recognition with Optics
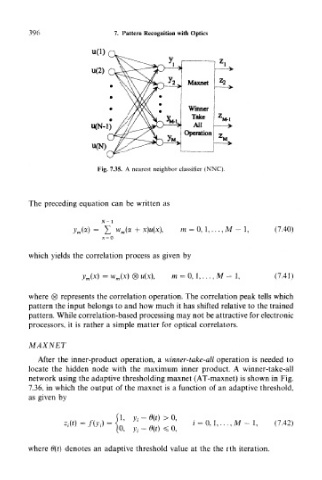
Fig. 7.35. A nearest neighbor classifier (NNC).
The preceding equation can be written as
N-l
w m(a + x)u(x), m = 0, 1,..., M — 1, (7.40)
which yields the correlation process as given by
y«(*) = *»(*) ® «(*), m - 0, 1,..., M - 1, (7.41)
where ® represents the correlation operation. The correlation peak tells which
pattern the input belongs to and how much it has shifted relative to the trained
pattern. While correlation-based processing may not be attractive for electronic
processors, it is rather a simple matter for optical correlators.
MAXNET
After the inner-product operation, a winner-take-all operation is needed to
locate the hidden node with the maximum inner product. A winner-take-all
network using the adaptive thresholding maxnet (AT-maxnet) is shown in Fig.
7.36, in which the output of the maxnet is a function of an adaptive threshold,
as given by
where B(t) denotes an adaptive threshold value at the the tth iteration.