Page 495 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 495
480 9. Computing with Optics
(a)
(b)
(c)
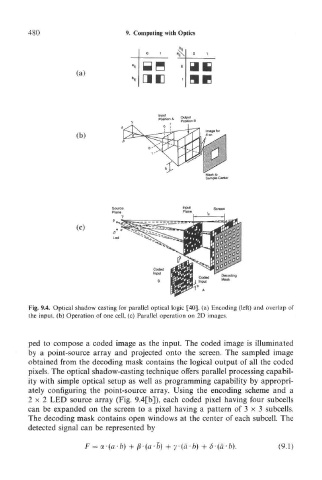
Fig. 9.4. Optical shadow casting for parallel optical logic [40]. (a) Encoding (left) and overlap of
the input, (b) Operation of one cell, (c) Parallel operation on 2D images.
ped to compose a coded image as the input. The coded image is illuminated
by a point-source array and projected onto the screen. The sampled image
obtained from the decoding mask contains the logical output of all the coded
pixels. The optical shadow-casting technique offers parallel processing capabil-
ity with simple optical setup as well as programming capability by appropri-
ately configuring the point-source array. Using the encoding scheme and a
2x 2 LED source array (Fig. 9.4[b]), each coded pixel having four subcells
can be expanded on the screen to a pixel having a pattern of 3 x 3 subcells.
The decoding mask contains open windows at the center of each subcell. The
detected signal can be represented by
= <x-(a-b) (d-b] + 6-(a-b) . (9.1)