Page 638 - Introduction to Information Optics
P. 638
62: 11. Information Display with Optics
E inc
E-2
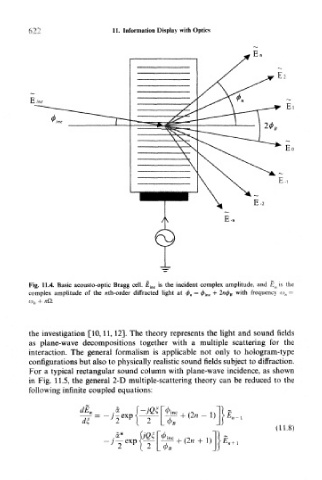
Fig. 11.4. Basic acousto-optic Bragg cell. £ inc is the incident complex amplitude, and E n is the
complex amplitude of the nth-order diffracted light at <j) n = <f>. mc + 2n4> B with frequency o) n ~-
feV, + n£l
the investigation [10,11,12]. The theory represents the light and sound fields
as plane-wave decompositions together with a multiple scattering for the
interaction. The general formalism is applicable not only to hologram-type
configurations but also to physically realistic sound fields subject to diffraction.
For a typical rectangular sound column with plane-wave incidence, as shown
in Fig. 11.5, the general 2-D multiple-scattering theory can be reduced to the
following infinite coupled equations:
dE
ex
./2 P f (In
(11.8)
-,/yexp (In H