Page 330 - Introduction to Marine Engineering
P. 330
304 Instrumentation and control
Boiler
load
Final load
Drum water Desired value
level Offset
Time
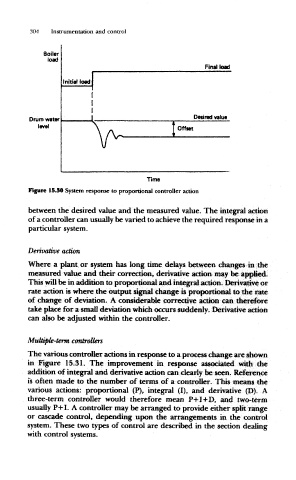
Figure 15.30 System response to proportional controller action
between the desired value and the measured value. The integral action
of a controller can usually be varied to achieve the required response in a
particular system.
Derivative action
Where a plant or system has long time delays between changes in the
measured value and their correction, derivative action may be applied.
This will be in addition to proportional and integral action. Derivative or
rate action is where the output signal change is proportional to the rate
of change of deviation. A considerable corrective action can therefore
take place for a small deviation which occurs suddenly. Derivative action
can also be adjusted within the controller.
Mttltipte-term controllers
The various controller actions in response to a process change are shown
in Figure 15.31. The improvement in response associated with the
addition of integral and derivative action can clearly be seen. Reference
is often made to the number of terms of a controller. This means the
various actions: proportional (P), integral (I), and derivative (D). A
three-term controller would therefore mean P-H-fD, and two-term
usually P+I. A controller may be arranged to provide either split range
or cascade control, depending upon the arrangements in the control
system. These two types of control are described in the section dealing
with control systems.