Page 135 - Introduction to Mineral Exploration
P. 135
118 M.K.G. WHATELEY
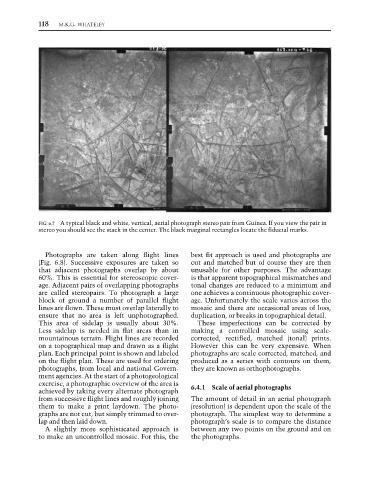
FIG. 6.7 A typical black and white, vertical, aerial photograph stereo pair from Guinea. If you view the pair in
stereo you should see the stack in the center. The black marginal rectangles locate the fiducial marks.
Photographs are taken along flight lines best fit approach is used and photographs are
(Fig. 6.8). Successive exposures are taken so cut and matched but of course they are then
that adjacent photographs overlap by about unusable for other purposes. The advantage
60%. This is essential for stereoscopic cover- is that apparent topographical mismatches and
age. Adjacent pairs of overlapping photographs tonal changes are reduced to a minimum and
are called stereopairs. To photograph a large one achieves a continuous photographic cover-
block of ground a number of parallel flight age. Unfortunately the scale varies across the
lines are flown. These must overlap laterally to mosaic and there are occasional areas of loss,
ensure that no area is left unphotographed. duplication, or breaks in topographical detail.
This area of sidelap is usually about 30%. These imperfections can be corrected by
Less sidelap is needed in flat areas than in making a controlled mosaic using scale-
mountainous terrain. Flight lines are recorded corrected, rectified, matched (tonal) prints.
on a topographical map and drawn as a flight However this can be very expensive. When
plan. Each principal point is shown and labeled photographs are scale corrected, matched, and
on the flight plan. These are used for ordering produced as a series with contours on them,
photographs, from local and national Govern- they are known as orthophotographs.
ment agencies. At the start of a photogeological
exercise, a photographic overview of the area is
achieved by taking every alternate photograph 6.4.1 Scale of aerial photographs
from successive flight lines and roughly joining The amount of detail in an aerial photograph
them to make a print laydown. The photo- (resolution) is dependent upon the scale of the
graphs are not cut, but simply trimmed to over- photograph. The simplest way to determine a
lap and then laid down. photograph’s scale is to compare the distance
A slightly more sophisticated approach is between any two points on the ground and on
to make an uncontrolled mosaic. For this, the the photographs.