Page 280 - Introduction to Mineral Exploration
P. 280
11: PROJECT EVALUATION 263
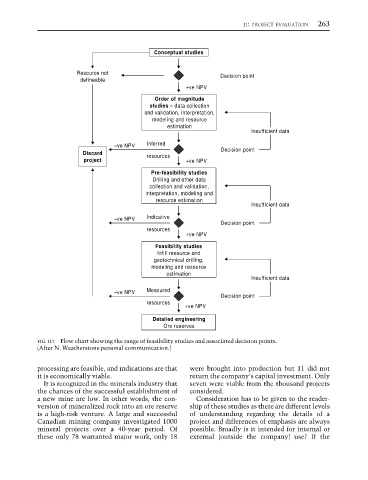
Conceptual studies
Resource not Decision point
defineable
+ve NPV
Order of magnitude
studies – data collection
and validation, interpretation,
modeling and resource
estimation
Insufficient data
–ve NPV Inferred
Decision point
Discard
resources
project +ve NPV
Pre-feasibility studies
Drilling and other data
collection and validation,
interpretation, modeling and
resource estimation
Insufficient data
–ve NPV Indicative
Decision point
resources
+ve NPV
Feasibility studies
Infill resource and
geotechnical drilling,
modeling and resource
estimation
Insufficient data
–ve NPV Measured
Decision point
resources
+ve NPV
Detailed engineering
Ore reserves
FIG. 11.7 Flow chart showing the range of feasibility studies and associated decision points.
(After N. Weatherstone personal communication.)
processing are feasible, and indications are that were brought into production but 11 did not
it is economically viable. return the company’s capital investment. Only
It is recognized in the minerals industry that seven were viable from the thousand projects
the chances of the successful establishment of considered.
a new mine are low. In other words, the con- Consideration has to be given to the reader-
version of mineralized rock into an ore reserve ship of these studies as there are different levels
is a high-risk venture. A large and successful of understanding regarding the details of a
Canadian mining company investigated 1000 project and differences of emphasis are always
mineral projects over a 40-year period. Of possible. Broadly is it intended for internal or
these only 78 warranted major work, only 18 external (outside the company) use? If the