Page 221 - Introduction to Petroleum Engineering
P. 221
208 UPSTREAM FACILITIES
Answer
A. 16wells 5000bbl/day/well 80000bbl/day.
B. No. The pipeline would have to be expanded or production from the wells
must be limited to 50 000 bbl liquid per day.
11.2 FLASH CALCULATION FOR SEPARATORS
The fluid stream produced from a well enters a separator where the fluid phases
separate. The focus of this section is the separation of the gas phase and the liquid
hydrocarbon phase. The compositions and volumes of the gas and liquid phases can
be estimated with a flash calculation. Flash calculations are also used in models of
many gas plant and refinery operations, as well as in compositional reservoir models.
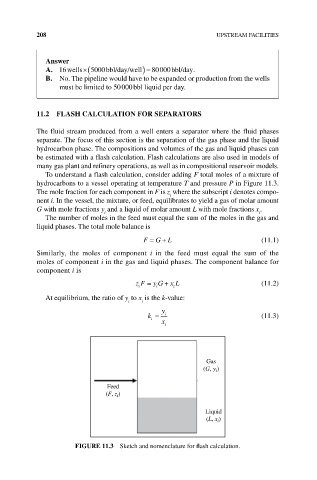
To understand a flash calculation, consider adding F total moles of a mixture of
hydrocarbons to a vessel operating at temperature T and pressure P in Figure 11.3.
The mole fraction for each component in F is z where the subscript i denotes compo-
i
nent i. In the vessel, the mixture, or feed, equilibrates to yield a gas of molar amount
G with mole fractions y and a liquid of molar amount L with mole fractions x . i
i
The number of moles in the feed must equal the sum of the moles in the gas and
liquid phases. The total mole balance is
F G L (11.1)
Similarly, the moles of component i in the feed must equal the sum of the
moles of component i in the gas and liquid phases. The component balance for
component i is
z F y Gx L (11.2)
i
i
i
At equilibrium, the ratio of y to x is the k‐value:
i i
y
k i i (11.3)
x i
Gas
(G, y i )
Feed
(F, z i )
Liquid
(L, x i )
FIgURE 11.3 Sketch and nomenclature for flash calculation.