Page 224 - Introduction to Petroleum Engineering
P. 224
PRESSURE RATING FOR SEPARATORS 211
Example 11.4 Flash Calculation
Complete the flash calculation for the mixture in the previous example. Verify
that G 089.
.
Answer
Use the kernel of Equation 11.9 to find the mole fractions x in the liquid
i
phase. Then use Equation 11.4 to find mole fractions y in the gas phase.
i
Vary G from 0.88 to 0.90 until the sums of x and y are both equal to 1.000.
i i
z
Mole x i i
Component Fraction z k‐Value 1 k i 1 G y i k x
i i
i
Methane 0.55 36.3 0.02 0.62
Propane 0.30 1.3 0.24 0.31
Normal pentane 0.15 0.1 0.74 0.07
11.3 PRESSURE RATINg FOR SEPARATORS
Separators and storage tanks on well locations are usually cylindrical in shape.
Storage tanks at refineries are mostly cylindrical, but some are spherical. These tanks
may be considered thin‐walled pressure vessels (Hibbeler, 2011) when the thickness
t of the wall is small relative to the inner radius of the cylinder r or sphere r . The
ic
is
thin‐walled criterion may be written as
t 01 or t 01 (11.12)
.
.
r ic r is
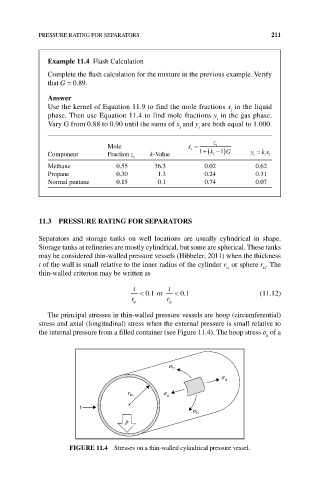
The principal stresses in thin‐walled pressure vessels are hoop (circumferential)
stress and axial (longitudinal) stress when the external pressure is small relative to
the internal pressure from a filled container (see Figure 11.4). The hoop stress σ of a
h
h
a
r ic a
t
h
p
FIgURE 11.4 Stresses on a thin‐walled cylindrical pressure vessel.