Page 91 - Introduction to chemical reaction engineering and kinetics
P. 91
4.3 Dependence of Rate on Concentration 73
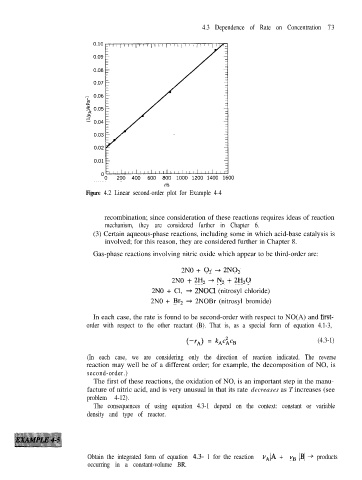
Figure 4.2 Linear second-order plot for Example 4-4
recombination; since consideration of these reactions requires ideas of reaction
mechanism, they are considered further in Chapter 6.
(3) Certain aqueous-phase reactions, including some in which acid-base catalysis is
involved; for this reason, they are considered further in Chapter 8.
Gas-phase reactions involving nitric oxide which appear to be third-order are:
2N0 + O2 + 2N0,
2N0 + 2H, -+ N, + 2H,O
2N0 + Cl, + 2NOCl (nitrosyl chloride)
2N0 + Br, + 2NOBr (nitrosyl bromide)
In each case, the rate is found to be second-order with respect to NO(A) and first-
order with respect to the other reactant (B). That is, as a special form of equation 4.1-3,
(-I*) = kAc;cg (4.3-1)
(In each case, we are considering only the direction of reaction indicated. The reverse
reaction may well be of a different order; for example, the decomposition of NO, is
second-order.)
The first of these reactions, the oxidation of NO, is an important step in the manu-
facture of nitric acid, and is very unusual in that its rate decreases as T increases (see
problem 4-12).
The consequences of using equation 4.3-1 depend on the context: constant or variable
density and type of reactor.
Obtain the integrated form of equation 4.3- 1 for the reaction ( v,lA + ) in IB + products
occurring in a constant-volume BR.