Page 100 -
P. 100
Knowledge Management Models 83
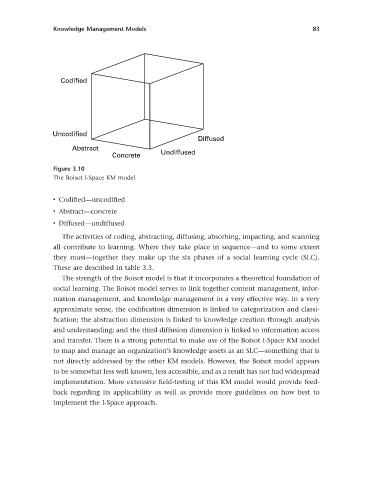
Codified
Uncodified
Diffused
Abstract
Concrete Undiffused
Figure 3.10
The Boisot I-Space KM model
• Codifi ed — uncodifi ed
• Abstract — concrete
• Diffused — undiffused
The activities of coding, abstracting, diffusing, absorbing, impacting, and scanning
all contribute to learning. Where they take place in sequence — and to some extent
they must — together they make up the six phases of a social learning cycle (SLC).
These are described in table 3.3 .
The strength of the Boisot model is that it incorporates a theoretical foundation of
social learning. The Boisot model serves to link together content management, infor-
mation management, and knowledge management in a very effective way. In a very
approximate sense, the codifi cation dimension is linked to categorization and classi-
fi cation; the abstraction dimension is linked to knowledge creation through analysis
and understanding; and the third diffusion dimension is linked to information access
and transfer. There is a strong potential to make use of the Boisot I-Space KM model
to map and manage an organization ’ s knowledge assets as an SLC — something that is
not directly addressed by the other KM models. However, the Boisot model appears
to be somewhat less well known, less accessible, and as a result has not had widespread
implementation. More extensive fi eld-testing of this KM model would provide feed-
back regarding its applicability as well as provide more guidelines on how best to
implement the I-Space approach.