Page 97 -
P. 97
80 Chapter 3
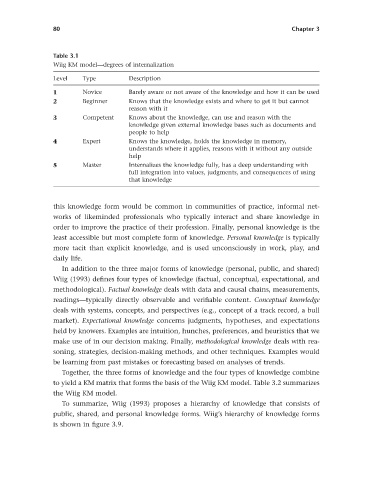
Table 3.1
Wiig KM model — degrees of internalization
Level Type Description
1 Novice Barely aware or not aware of the knowledge and how it can be used
2 Beginner Knows that the knowledge exists and where to get it but cannot
reason with it
3 Competent Knows about the knowledge, can use and reason with the
knowledge given external knowledge bases such as documents and
people to help
4 Expert Knows the knowledge, holds the knowledge in memory,
understands where it applies, reasons with it without any outside
help
5 Master Internalizes the knowledge fully, has a deep understanding with
full integration into values, judgments, and consequences of using
that knowledge
this knowledge form would be common in communities of practice, informal net-
works of likeminded professionals who typically interact and share knowledge in
order to improve the practice of their profession. Finally, personal knowledge is the
least accessible but most complete form of knowledge. Personal knowledge is typically
more tacit than explicit knowledge, and is used unconsciously in work, play, and
daily life.
In addition to the three major forms of knowledge (personal, public, and shared)
Wiig (1993) defi nes four types of knowledge (factual, conceptual, expectational, and
methodological). Factual knowledge deals with data and causal chains, measurements,
readings — typically directly observable and verifi able content. Conceptual knowledge
deals with systems, concepts, and perspectives (e.g., concept of a track record, a bull
market). Expectational knowledge concerns judgments, hypotheses, and expectations
held by knowers. Examples are intuition, hunches, preferences, and heuristics that we
make use of in our decision making. Finally, methodological knowledge deals with rea-
soning, strategies, decision-making methods, and other techniques. Examples would
be learning from past mistakes or forecasting based on analyses of trends.
Together, the three forms of knowledge and the four types of knowledge combine
to yield a KM matrix that forms the basis of the Wiig KM model. Table 3.2 summarizes
the Wiig KM model.
To summarize, Wiig (1993) proposes a hierarchy of knowledge that consists of
public, shared, and personal knowledge forms. Wiig ’ s hierarchy of knowledge forms
is shown in fi gure 3.9 .