Page 96 -
P. 96
Knowledge Management Models 79
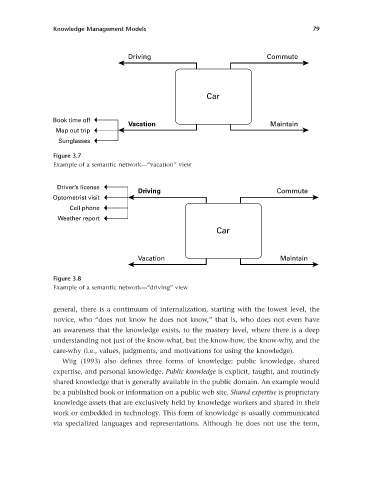
Driving Commute
Car
Book time off
Vacation Maintain
Map out trip
Sunglasses
Figure 3.7
Example of a semantic network — “ vacation ” view
Driver’s license
Driving Commute
Optometrist visit
Cell phone
Weather report
Car
Vacation Maintain
Figure 3.8
Example of a semantic network — “ driving ” view
general, there is a continuum of internalization, starting with the lowest level, the
novice, who “ does not know he does not know, ” that is, who does not even have
an awareness that the knowledge exists, to the mastery level, where there is a deep
understanding not just of the know-what, but the know-how, the know-why, and the
care-why (i.e., values, judgments, and motivations for using the knowledge).
Wiig (1993) also defi nes three forms of knowledge: public knowledge, shared
expertise, and personal knowledge. Public knowledge is explicit, taught, and routinely
shared knowledge that is generally available in the public domain. An example would
be a published book or information on a public web site. Shared expertise is proprietary
knowledge assets that are exclusively held by knowledge workers and shared in their
work or embedded in technology. This form of knowledge is usually communicated
via specialized languages and representations. Although he does not use the term,