Page 295 - Laboratory Manual in Physical Geology
P. 295
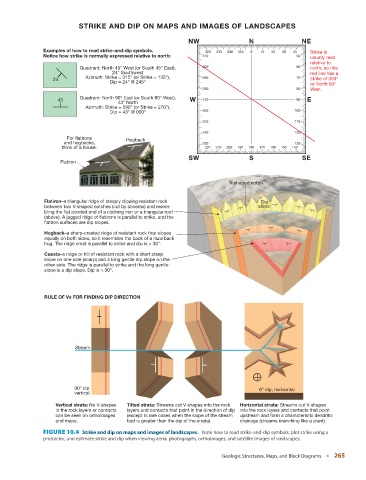
STRIKE AND DIP ON MAPS AND IMAGES OF LANDSCAPES
NW N NE
Examples of how to read strike-and-dip symbols. 320 330 340 350 0 10 20 30 40 Strike is
Notice how strike is normally expressed relative to north: 310 50 usually read
relative to
Quadrant: North 45° West (or South 45° East), 300 60 north, so this
24° Southwest red line has a
Azimuth: Strike = 315° (or Strike = 135°), 290 70
24 strike of 300°
Dip = 24° @ 245°
or North 60°
280 80 West.
Quadrant: North 90° East (or South 90° West),
43 W 270 90 E
43° North
Azimuth: Strike = 090° (or Strike = 270°),
Dip = 43° @ 000° 260 100
250 110
240 120
For flatirons Hogback
and hogbacks, 230 130
think of a house. 220 210 200 190 180 170 160 150 140
SW S SE
Flatiron
V-shaped notch
Flatiron–a triangular ridge of steeply dipping resistant rock Dip
between two V-shaped notches (cut by streams) and resem- slope
bling the flat pointed end of a clothing iron or a triangular roof
(above). A jagged ridge of flatirons is parallel to strike, and the
flatiron surfaces are dip slopes.
Hogback–a sharp-crested ridge of resistant rock that slopes
equally on both sides, so it resembles the back of a razorback
hog. The ridge crest is parallel to strike and dip is > 30°.
Cuesta–a ridge or hill of resistant rock with a short steep
slope on one side (scarp) and a long gentle dip slope on the
other side. The ridge is parallel to strike and the long gentle
slope is a dip slope. Dip is < 30°.
RULE OF Vs FOR FINDING DIP DIRECTION
Stream
90° dip 0° dip, horizontal
vertical
Vertical strata: No V-shapes Tilted strata: Streams cut V-shapes into the rock Horizontal strata: Streams cut V-shapes
in the rock layers or contacts layers and contacts that point in the direction of dip into the rock layers and contacts that point
can be seen on orthoimages (except in rare cases when the slope of the stream upstream and form a characteristic dendritic
and maps. bed is greater than the dip of the strata). drainage (streams branching like a plant).
FIGURE 10.4 Strike and dip on maps and images of landscapes. Note how to read strike-and-dip symbols, plot strike using a
protractor, and estimate strike and dip when viewing aerial photographs, orthoimages, and satellite images of landscapes.
Geologic Structures, Maps, and Block Diagrams ■ 265