Page 291 - Laboratory Manual in Physical Geology
P. 291
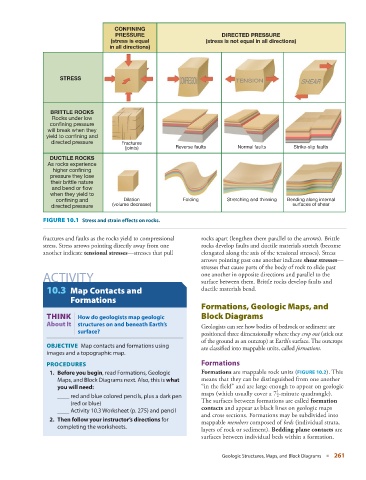
CONFINING
PRESSURE DIRECTED PRESSURE
(stress is equal (stress is not equal in all directions)
in all directions)
STRESS COMPRESSION TENSION SHEAR
BRITTLE ROCKS
Rocks under low
confining pressure
will break when they
yield to confining and
directed pressure Fractures
(joints) Reverse faults Normal faults Strike-slip faults
DUCTILE ROCKS
As rocks experience
higher confining
pressure they lose
their brittle nature
and bend or flow
when they yield to
Dilation
confining and (volume decrease) Folding Stretching and thinning Bending along internal
surfaces of shear
directed pressure
FIGURE 10.1 Stress and strain effects on rocks.
fractures and faults as the rocks yield to compressional rocks apart (lengthen them parallel to the arrows). Brittle
stress. Stress arrows pointing directly away from one rocks develop faults and ductile materials stretch (become
another indicate tensional stresses —stresses that pull elongated along the axis of the tensional stresses). Stress
arrows pointing past one another indicate shear stresses —
stresses that cause parts of the body of rock to slide past
ACTIVITY one another in opposite directions and parallel to the
surface between them. Brittle rocks develop faults and
10.3 Map Contacts and ductile materials bend.
Formations
Formations, Geologic Maps, and
THINK | How do geologists map geologic Block Diagrams
About It structures on and beneath Earth’s Geologists can see how bodies of bedrock or sediment are
surface? positioned three dimensionally where they crop out (stick out
of the ground as an outcrop) at Earth’s surface. The outcrops
OBJECTIVE Map contacts and formations using
are classified into mappable units, called formations.
images and a topographic map.
PROCEDURES Formations
1. Before you begin , read Formations, Geologic Formations are mappable rock units ( FIGURE 10.2 ). This
Maps, and Block Diagrams next. Also, this is what means that they can be distinguished from one another
you will need: “in the field” and are large enough to appear on geologic
1
maps (which usually cover a 7 -minute quadrangle).
____ red and blue colored pencils, plus a dark pen 2
(red or blue) The surfaces between formations are called formation
____ Activity 10.3 Worksheet (p. 275 ) and pencil contacts and appear as black lines on geologic maps
and cross sections. Formations may be subdivided into
2. Then follow your instructor’s directions for mappable members composed of beds (individual strata,
completing the worksheets.
layers of rock or sediment). Bedding plane contacts are
surfaces between individual beds within a formation.
Geologic Structures, Maps, and Block Diagrams ■ 261