Page 118 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 118
104 K. T. Lee and C. Ofori-Boateng
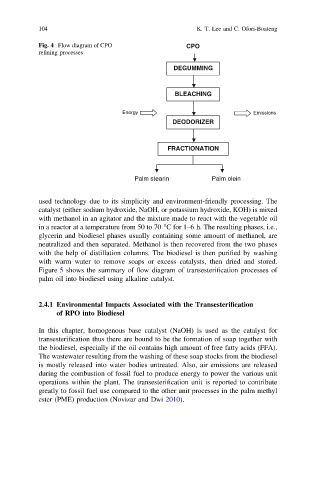
Fig. 4 Flow diagram of CPO CPO
refining processes
DEGUMMING
BLEACHING
Energy Emissions
DEODORIZER
FRACTIONATION
Palm stearin Palm olein
used technology due to its simplicity and environment-friendly processing. The
catalyst (either sodium hydroxide, NaOH, or potassium hydroxide, KOH) is mixed
with methanol in an agitator and the mixture made to react with the vegetable oil
in a reactor at a temperature from 50 to 70 °C for 1–6 h. The resulting phases, i.e.,
glycerin and biodiesel phases usually containing some amount of methanol, are
neutralized and then separated. Methanol is then recovered from the two phases
with the help of distillation columns. The biodiesel is then purified by washing
with warm water to remove soaps or excess catalysts, then dried and stored.
Figure 5 shows the summary of flow diagram of transesterification processes of
palm oil into biodiesel using alkaline catalyst.
2.4.1 Environmental Impacts Associated with the Transesterification
of RPO into Biodiesel
In this chapter, homogenous base catalyst (NaOH) is used as the catalyst for
transesterification thus there are bound to be the formation of soap together with
the biodiesel, especially if the oil contains high amount of free fatty acids (FFA).
The wastewater resulting from the washing of these soap stocks from the biodiesel
is mostly released into water bodies untreated. Also, air emissions are released
during the combustion of fossil fuel to produce energy to power the various unit
operations within the plant. The transesterification unit is reported to contribute
greatly to fossil fuel use compared to the other unit processes in the palm methyl
ester (PME) production (Novizar and Dwi 2010).