Page 119 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 119
Life Cycle Assessment of Biodiesel from Palm Oil 105
Catalyst
Methanol MIXER
Methanol
REACTOR
Methanol NEUTRALIZER Glycerin
Glycerin
&
methanol
PHASE SEPARATOR METHANOL
RECOVERY
Biodiesel & methanol
METHANOL
PURIFIER DRYER
RECOVERY
Biodiesel
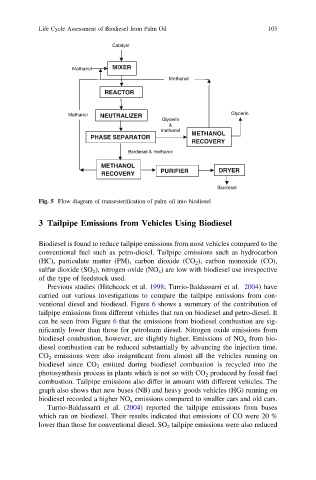
Fig. 5 Flow diagram of transesterification of palm oil into biodiesel
3 Tailpipe Emissions from Vehicles Using Biodiesel
Biodiesel is found to reduce tailpipe emissions from most vehicles compared to the
conventional fuel such as petro-diesel. Tailpipe emissions such as hydrocarbon
(HC), particulate matter (PM), carbon dioxide (CO 2 ), carbon monoxide (CO),
sulfur dioxide (SO 2 ), nitrogen oxide (NO x ) are low with biodiesel use irrespective
of the type of feedstock used.
Previous studies (Hitchcock et al. 1998; Turrio-Baldassarri et al. 2004) have
carried out various investigations to compare the tailpipe emissions from con-
ventional diesel and biodiesel. Figure 6 shows a summary of the contribution of
tailpipe emissions from different vehicles that run on biodiesel and petro-diesel. It
can be seen from Figure 6 that the emissions from biodiesel combustion are sig-
nificantly lower than those for petroleum diesel. Nitrogen oxide emissions from
biodiesel combustion, however, are slightly higher. Emissions of NO x from bio-
diesel combustion can be reduced substantially by advancing the injection time.
CO 2 emissions were also insignificant from almost all the vehicles running on
biodiesel since CO 2 emitted during biodiesel combustion is recycled into the
photosynthesis process in plants which is not so with CO 2 produced by fossil fuel
combustion. Tailpipe emissions also differ in amount with different vehicles. The
graph also shows that new buses (NB) and heavy goods vehicles (HG) running on
biodiesel recorded a higher NO x emissions compared to smaller cars and old cars.
Turrio-Baldassarri et al. (2004) reported the tailpipe emissions from buses
which ran on biodiesel. Their results indicated that emissions of CO were 20 %
lower than those for conventional diesel. SO 2 tailpipe emissions were also reduced