Page 253 - Lindens Handbook of Batteries
P. 253
MAGNeSiUM AND ALUMiNUM bATTerieS 10.5
an extruded mix of manganese dioxide, acetylene black for conductivity and moisture retention,
barium chromate (an inhibitor), and magnesium hydroxide (a pH buffer). The electrolyte is an
aqueous solution of magnesium perchlorate with lithium chromate. A carbon rod serves as the
cathode current collector. The separator is an absorbent kraft paper as in the paper-lined zinc
battery structure. Sealing of the magnesium battery is critical, as it must be tight to retain bat-
tery moisture during storage but provide a means for the escape of hydrogen gas which forms as
the result of the corrosion reaction during the discharge. This is accomplished by a mechanical
vent—a small hole in the plastic top seal washer under the retainer ring which is deformed under
pressure, releasing the excess gas. 8
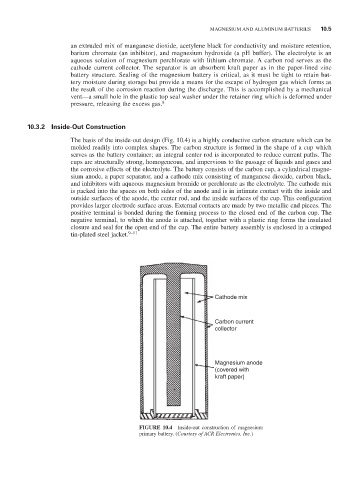
10.3.2 Inside-Out Construction
The basis of the inside-out design (Fig. 10.4) is a highly conductive carbon structure which can be
molded readily into complex shapes. The carbon structure is formed in the shape of a cup which
serves as the battery container; an integral center rod is incorporated to reduce current paths. The
cups are structurally strong, homogeneous, and impervious to the passage of liquids and gases and
the corrosive effects of the electrolyte. The battery consists of the carbon cup, a cylindrical magne-
sium anode, a paper separator, and a cathode mix consisting of manganese dioxide, carbon black,
and inhibitors with aqueous magnesium bromide or perchlorate as the electrolyte. The cathode mix
is packed into the spaces on both sides of the anode and is in intimate contact with the inside and
outside surfaces of the anode, the center rod, and the inside surfaces of the cup. This configuration
provides larger electrode surface areas. external contacts are made by two metallic end pieces. The
positive terminal is bonded during the forming process to the closed end of the carbon cup. The
negative terminal, to which the anode is attached, together with a plastic ring forms the insulated
closure and seal for the open end of the cup. The entire battery assembly is enclosed in a crimped
tin-plated steel jacket. 9–11
Cathode mix
Carbon current
collector
Magnesium anode
(covered with
kraft paper)
FIGURE 10.4 inside-out construction of magnesium
primary battery. (Courtesy of ACR Electronics, Inc.)