Page 278 - Lindens Handbook of Batteries
P. 278
11.16 pRIMARy BATTERIES
O + 2 H O + 4e = 4 OH – polymer gasket material, as well as the choice
–
2
2
of the anode gelling agent and possible damage
to the seal area during cell manufacture.
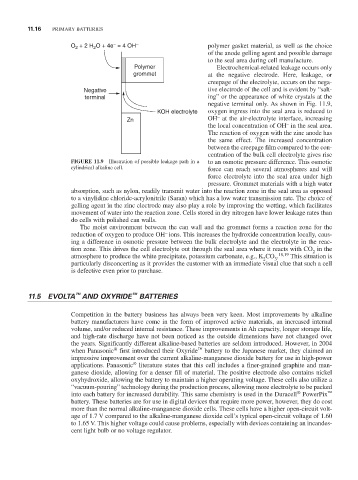
Polymer Electrochemical-related leakage occurs only
Polymer
Grommet at the negative electrode. Here, leakage, or
grommet
creepage of the electrolyte, occurs on the nega-
Negative tive electrode of the cell and is evident by “salt-
terminal ing” or the appearance of white crystals at the
negative terminal only. As shown in Fig. 11.9,
KOH electrolyte oxygen ingress into the seal area is reduced to
-
Zn OH at the air-electrolyte interface, increasing
-
the local concentration of OH in the seal area.
The reaction of oxygen with the zinc anode has
the same effect. The increased concentration
between the creepage film compared to the con-
centration of the bulk cell electrolyte gives rise
FiguRE 11.9 Illustration of possible leakage path in a to an osmotic pressure difference. This osmotic
cylindrical alkaline cell. force can reach several atmospheres and will
force electrolyte into the seal area under high
pressure. Grommet materials with a high water
absorption, such as nylon, readily transmit water into the reaction zone in the seal area as opposed
to a vinylidine chloride-acrylonitrile (Saran) which has a low water transmission rate. The choice of
gelling agent in the zinc electrode may also play a role by improving the wetting, which facilitates
movement of water into the reaction zone. Cells stored in dry nitrogen have lower leakage rates than
do cells with polished can walls.
The moist environment between the can wall and the grommet forms a reaction zone for the
-
reduction of oxygen to produce OH ions. This increases the hydroxide concentration locally, caus-
ing a difference in osmotic pressure between the bulk electrolyte and the electrolyte in the reac-
tion zone. This drives the cell electrolyte out through the seal area where it reacts with CO in the
2
atmosphere to produce the white precipitate, potassium carbonate, e.g., K CO . 18,19 This situation is
3
2
particularly disconcerting as it provides the customer with an immediate visual clue that such a cell
is defective even prior to purchase.
™
11.5 EVOLTA AND OxyRIDE BATTERIES
™
Competition in the battery business has always been very keen. Most improvements by alkaline
battery manufacturers have come in the form of improved active materials, an increased internal
volume, and/or reduced internal resistance. These improvements in Ah capacity, longer storage life,
and high-rate discharge have not been noticed as the outside dimensions have not changed over
the years. Significantly different alkaline-based batteries are seldom introduced. However, in 2004
when panasonic first introduced their Oxyride battery to the Japanese market, they claimed an
®
™
impressive improvement over the current alkaline-manganese dioxide battery for use in high-power
applications. panasonic literature states that this cell includes a finer-grained graphite and man-
®
ganese dioxide, allowing for a denser fill of material. The positive electrode also contains nickel
oxyhydroxide, allowing the battery to maintain a higher operating voltage. These cells also utilize a
“vacuum-pouring” technology during the production process, allowing more electrolyte to be packed
™
®
into each battery for increased durability. This same chemistry is used in the Duracell powerpix
battery. These batteries are for use in digital devices that require more power, however, they do cost
more than the normal alkaline-manganese dioxide cells. These cells have a higher open-circuit volt-
age of 1.7 V compared to the alkaline-manganese dioxide cell’s typical open-circuit voltage of 1.60
to 1.65 V. This higher voltage could cause problems, especially with devices containing an incandes-
cent light bulb or no voltage regulator.