Page 291 - Lindens Handbook of Batteries
P. 291
MERCURIC OXIDE BATTERIES 12.11
12.5.5 Storage
Zinc/mercuric oxide batteries have good storage characteristics. In general they will store for over
2 years at 20°C with a capacity loss of 10 to 20% and 1 year at 45°C with about a 20% loss.
Storage at lower temperatures, such as down to -20°C, will, as with other battery systems,
increase storage life.
The storability will depend on the discharge load and also on the cell structure. Failure in stor-
age is usually due to the breakdown of cellulosic compounds within the cell which, at first, results
in a reduction of the limiting-current density at the anode. Further breakdown produces low-drain
internal electrical paths and a real loss of capacity due to self-discharge. Eventually, complete self-
discharge can occur, but at 20°C and below these processes take many years.
Long storage lives are within the capabilities of the mercuric oxide system. For example, a
wound-anode cell with a noncellulosic barrier has a capacity loss in the region of only 15% over
6 years. With cells designed for long-term storage, dissolution of mercuric oxide from the cathode
and its transfer to the anode become a significant factor in capacity loss.
12.5.6 Service Life
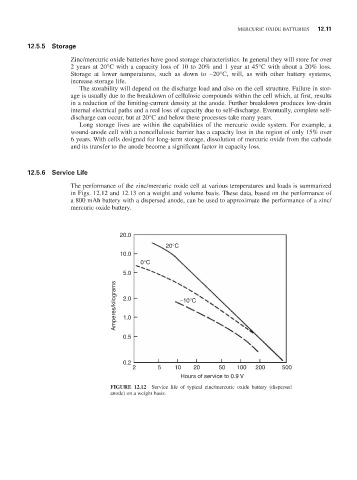
The performance of the zinc/mercuric oxide cell at various temperatures and loads is summarized
in Figs. 12.12 and 12.13 on a weight and volume basis. These data, based on the performance of
a 800 mAh battery with a dispersed anode, can be used to approximate the performance of a zinc/
mercuric oxide battery.
20.0
20°C
10.0
0°C
5.0
Amperes/kilograms 2.0 –10°C
1.0
0.5
0.2
2 5 10 20 50 100 200 500
Hours of service to 0.9 V
FIGURE 12.12 Service life of typical zinc/mercuric oxide battery (dispersed
anode) on a weight basis.