Page 345 - Lindens Handbook of Batteries
P. 345
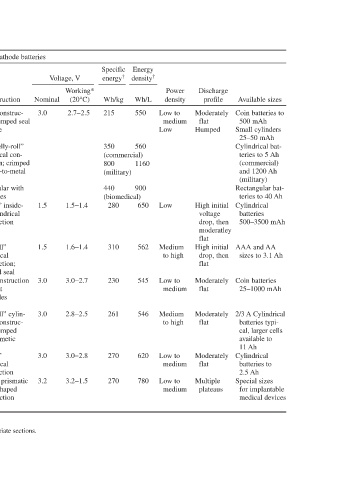
Available sizes Coin batteries to 500 mAh Small cylinders 25–50 mAh Cylindrical bat- teries to 5 Ah (commercial) and 1200 Ah (military) rectangular bat- teries to 40 Ah Cylindrical batteries 500–3500 mAh AAA and AA sizes to 3.1 Ah Coin batteries 25–1000 mAh 2/3 A Cylindrical batteries typi- cal, larger cells available to 11 Ah Cylindrical batteries to 2.5 Ah Special sizes for implantable medical devices
Discharge profile Moderately flat Humped High initial voltage drop, then moderatley flat High initial drop, then flat Moderately flat Moderately flat Moderately flat Multiple plateaus
Power density Low to medium Low Low Medium to high Low to medium Medium to high Low to medium Low to medium
energy density † Wh/L 550 560 1160 900 650 562 545 546 620 780
Specific energy † Wh/kg 215 350 (commercial) 800 (military) 440 (biomedical) 280 310 230 261 270 270
Working* (20°C) 2.7-2.5 1.5-1.4 1.6-1.4 3.0-2.7 2.8-2.5 3.0-2.8 3.2-1.5
Voltage, V Nominal 3.0 1.5 1.5 3.0 3.0 3.0 3.2
Solid cathode batteries Construction “Coin” construc- tion; crimped seal Pin type Spiral “jelly-roll” cylindrical con- struction; crimped or glass-to-metal seal rectangular with flat plates “Bobbin” inside- out cylindrical construction “Jelly-roll” cylindrical construction; crimped seal “Coin construction with flat electrodes “Jelly-roll” cylin- drical construc- tion; crimped and hermetic seals “Bobbin” cylindrical construction rounded prismatic and D-shap
Characteristics of Lithium Primary Batteries (Continued )
Separator Polypropylene Nonwoven glass Microporous polyethylene Polypropylene Polypropylene Polypropylene Microporous polypropylene
Solute LiBF 4 or LiAsF 6 LiClO 4 Lii Li salt Li salt Li salt LiAsF 6
electrolyte Solvent PC + DMe or BL 1,3D 1–3D + DMe PC + DMe Organic solvent Organic solvent PC, DMe † energy densities are for 20°C, under favorable discharge conditions. See details in appropriate sections.
Cathode CFx with carbon and binder on nickel collector CuO pressed in cell can FeS 2 with carbon and binders MnO 2 with carbon and binder on sup- porting grid AgV 2 O 5.5 with graphite and carbon *Working voltages are typical for discharges at favorable loads.
TABLE 14.6 System Lithium/carbon mono-fluoride Li/CFx Lithium/ copper oxide (Li/CuO) Lithium/iron disulfide (LiFeS 2) Lithium/ manganese dioxide (Li/MnO 2 Lithium/silver vanadium oxide (Li/ AgV 4 O 11)
14.10