Page 344 - Lindens Handbook of Batteries
P. 344
energy
density †
Specific
energy †
Voltage, V
Solid cathode batteries
Characteristics of Lithium Primary Batteries (Continued )
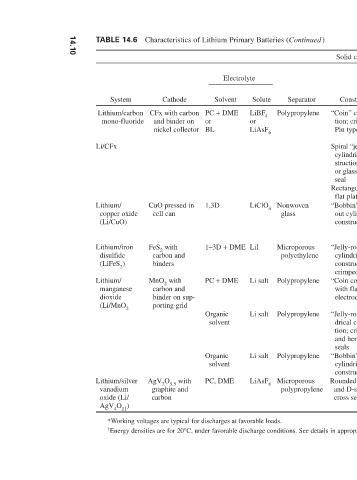
Separator Discharge Power Working* Available sizes profile density Wh/L Wh/kg (20°C) Nominal Construction Coin batteries to Moderately Low to 550 215 2.7-2.5 3.0 “Coin” construc- Polypropylene 500 mAh flat medium tion; crimped seal Small cylinders Humped Low Pin type 25–50 mAh Cylindrical bat- 560 350 Spiral “jelly-roll” teries to 5 Ah cylindrical con- (commercial) (commercial) struction; crimped 1160 800 and 1200 Ah or glass-to-metal (military)
Solute LiBF 4 or LiAsF 6 LiClO 4 Lii Li salt Li salt Li salt LiAsF 6 † energy densities are for 20°C, under favorable discharge conditions. See details in appropriate sections.
electrolyte Solvent PC + DMe or BL 1,3D 1–3D + DMe PC + DMe Organic solvent Organic solvent PC, DMe
CFx with carbon nickel collector *Working voltages are typical for discharges at favorable loads.
Cathode and binder on CuO pressed in cell can FeS 2 with carbon and binders MnO 2 with carbon and binder on sup- porting grid AgV 2 O 5.5 with graphite and carbon
TABLE 14.6 System Lithium/carbon mono-fluoride Li/CFx Lithium/ copper oxide (Li/CuO) Lithium/iron disulfide (LiFeS 2) Lithium/ manganese dioxide (Li/MnO 2 Lithium/silver vanadium oxide (Li/ AgV 4O 11)
14.10