Page 372 - Lindens Handbook of Batteries
P. 372
LiTHiUM PriMAry BATTerieS 14.37
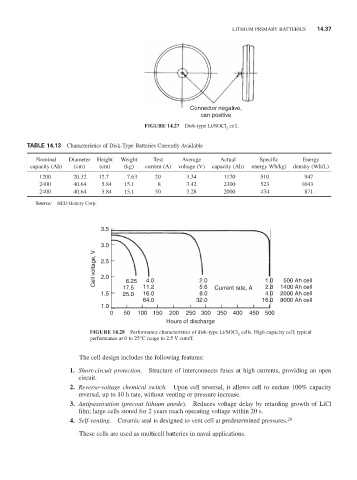
Connector negative,
can positive
FIGURE 14.27 Disk-type Li/SOCl cell.
2
TABLE 14.13 Characteristics of Disk-Type Batteries Currently Available
Nominal Diameter Height Weight Test Average Actual Specific energy
capacity (Ah) (cm) (cm) (kg) current (A) voltage (V) capacity (Ah) energy Wh/kg) density (Wh/L)
1200 20.32 12.7 7.63 20 3.34 1170 510 947
2400 40.64 5.84 15.1 8 3.42 2300 523 1043
2400 40.64 5.84 15.1 50 3.28 2000 434 871
Source: HeD Battery Corp.
3.5
3.0
Cell voltage, V 2.5 6.25 4.0 2.0 1.0 500 Ah cell
2.0
16.0
1.5 17.5 11.2 5.6 Current rate, A 2.8 1400 Ah cell
2000 Ah cell
4.0
8.0
25.0
64.0 32.0 16.0 8000 Ah cell
1.0
0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500
Hours of discharge
FIGURE 14.28 Performance characteristics of disk-type Li/SOCl cells. High-capacity cell; typical
2
performance at 0 to 25°C range to 2.5 V cutoff.
The cell design includes the following features:
1. Short-circuit protection. Structure of interconnects fuses at high currents, providing an open
circuit.
2. Reverse-voltage chemical switch. Upon cell reversal, it allows cell to endure 100% capacity
reversal, up to 10 h rate, without venting or pressure increase.
3. Antipassivation (precoat lithium anode). reduces voltage delay by retarding growth of LiCl
film; large cells stored for 2 years reach operating voltage within 20 s.
4. Self-venting. Ceramic seal is designed to vent cell at predetermined pressures. 28
These cells are used as multicell batteries in naval applications.