Page 398 - Lindens Handbook of Batteries
P. 398
LiTHiUM PriMAry BATTerieS 14.63
The low-capacity Li/MnO batteries can generally be handled without hazard, but, as with the
2
conventional primary battery systems, charging and incineration should be avoided as these condi-
tions could cause a cell to explode.
The higher-capacity cylindrical batteries are generally equipped with a venting mechanism
to prevent explosion, but the batteries, nevertheless, should be protected to avoid short circuits
and cell reversal, as well as charging and incineration. Most of the high-rate batteries are also
equipped with an internal resettable current and thermal protective system called a positive
temperature coefficient (PTC) device. When a cell is short-circuited or discharged above design
limits and the cell temperature increases, the resistance of the PTC device quickly increases sig-
nificantly. This limits the amount of current that can be drawn from the cell and keeps the internal
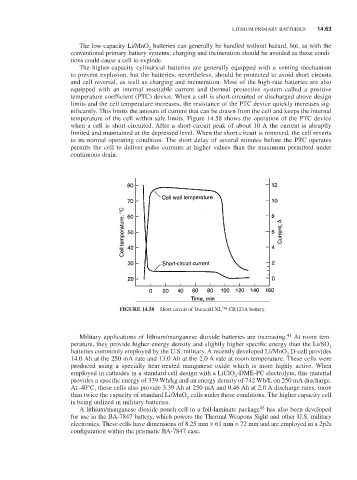
temperature of the cell within safe limits. Figure 14.58 shows the operation of the PTC device
when a cell is short-circuited. After a short-circuit peak of about 10 A the current is abruptly
limited and maintained at the depressed level. When the short circuit is removed, the cell reverts
to its normal operating condition. The short delay of several minutes before the PTC operates
permits the cell to deliver pulse currents at higher values than the maximum permitted under
continuous drain.
FIGURE 14.58 Short circuit of Duracell XL™ Cr123A battery.
41
Military applications of lithium/manganese dioxide batteries are increasing. At room tem-
perature, they provide higher energy density and slightly higher specific energy than the Li/SO
2
batteries commonly employed by the U.S. military. A recently developed Li/MnO D-cell provides
2
14.0 Ah at the 250 mA rate and 13.0 Ah at the 2.0 A rate at room temperature. These cells were
produced using a specially heat-treated manganese oxide which is more highly active. When
employed in cathodes in a standard cell design with a LiClO -DMe-PC electrolyte, this material
4
provides a specific energy of 339 Wh/kg and an energy density of 742 Wh/L on 250 mA discharge.
At–40°C, these cells also provide 3.39 Ah at 250 mA and 0.46 Ah at 2.0 A discharge rates, more
than twice the capacity of standard Li/MnO cells under these conditions. The higher capacity cell
2
is being utilized in military batteries.
42
A lithium/manganese dioxide pouch cell in a foil-laminate package has also been developed
for use in the BA-7847 battery, which powers the Thermal Weapons Sight and other U.S. military
electronics. These cells have dimensions of 8.25 mm × 61 mm × 72 mm and are employed in a 2p2s
configuration within the prismatic BA-7847 case.