Page 406 - Lindens Handbook of Batteries
P. 406
LiTHiUM PriMAry BATTerieS 14.71
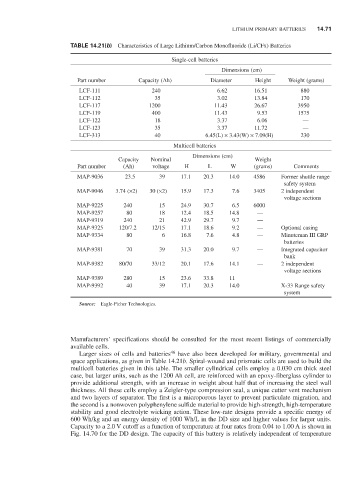
TABLE 14.21(b) Characteristics of Large Lithium/Carbon Monofluoride (Li/CFx) Batteries
Single-cell batteries
Dimensions (cm)
Part number Capacity (Ah) Diameter Height Weight (grams)
LCF-111 240 6.62 16.51 880
LCF-112 35 3.02 13.84 170
LCF-117 1200 11.43 26.67 3950
LCF-119 400 11.43 9.53 1575
LCF-122 18 3.37 6.06 —
LCF-123 35 3.37 11.72 —
LCF-313 40 6.45(L) × 3.43(W) × 7.09(H) 230
Multicell batteries
Dimensions (cm)
Capacity Nominal Weight
Part number (Ah) voltage H L W (grams) Comments
MAP-9036 23.5 39 17.1 20.3 14.0 4586 Former shuttle range
safety system
MAP-9046 3.74 (×2) 30 (×2) 15.9 17.3 7.6 3405 2 independent
voltage sections
MAP-9225 240 15 24.9 30.7 6.5 6000
MAP-9257 80 18 12.4 18.5 14.8 —
MAP-9319 240 21 42.9 29.7 9.7 —
MAP-9325 120/7.2 12/15 17.1 18.6 9.2 — Optional casing
MAP-9334 80 6 16.8 7.6 4.8 — Minuteman iii GrP
batteries
MAP-9381 70 39 31.3 20.0 9.7 — integrated capacitor
bank
MAP-9382 80/70 33/12 20.1 17.6 14.1 — 2 independent
voltage sections
MAP-9389 280 15 23.6 33.8 11
MAP-9392 40 39 17.1 20.3 14.0 X-33 range safety
system
Source: eagle-Picher Technologies.
Manufacturers’ specifications should be consulted for the most recent listings of commercially
available cells.
46
Larger sizes of cells and batteries have also been developed for military, governmental and
space applications, as given in Table 14.21b. Spiral-wound and prismatic cells are used to build the
multicell batteries given in this table. The smaller cylindrical cells employ a 0.030 cm thick steel
case, but larger units, such as the 1200 Ah cell, are reinforced with an epoxy-fiberglass cylinder to
provide additional strength, with an increase in weight about half that of increasing the steel wall
thickness. All these cells employ a Zeigler-type compression seal, a unique cutter vent mechanism
and two layers of separator. The first is a microporous layer to prevent particulate migration, and
the second is a nonwoven polyphenylene sulfide material to provide high-strength, high-temperature
stability and good electrolyte wicking action. These low-rate designs provide a specific energy of
600 Wh/kg and an energy density of 1000 Wh/L in the DD size and higher values for larger units.
Capacity to a 2.0 V cutoff as a function of temperature at four rates from 0.04 to 1.00 A is shown in
Fig. 14.70 for the DD design. The capacity of this battery is relatively independent of temperature