Page 94 - Lindens Handbook of Batteries
P. 94
FACTORS AFFECTING BATTERY PERFORMANCE 3.13
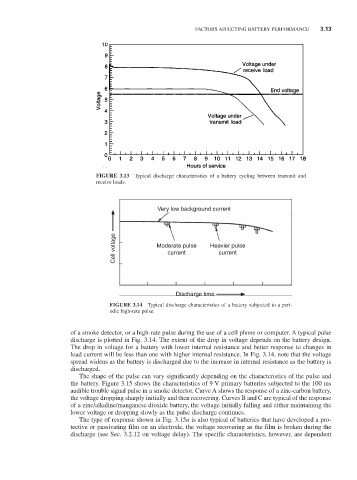
FIGURE 3.13 Typical discharge characteristics of a battery cycling between transmit and
receive loads.
Very low background current
Cell voltage Moderate pulse Heavier pulse
current
current
Discharge time
FIGURE 3.14 Typical discharge characteristics of a battery subjected to a peri-
odic high-rate pulse.
of a smoke detector, or a high-rate pulse during the use of a cell phone or computer. A typical pulse
discharge is plotted in Fig. 3.14. The extent of the drop in voltage depends on the battery design.
The drop in voltage for a battery with lower internal resistance and better response to changes in
load current will be less than one with higher internal resistance. In Fig. 3.14, note that the voltage
spread widens as the battery is discharged due to the increase in internal resistance as the battery is
discharged.
The shape of the pulse can vary significantly depending on the characteristics of the pulse and
the battery. Figure 3.15 shows the characteristics of 9 V primary batteries subjected to the 100 ms
audible trouble signal pulse in a smoke detector. Curve A shows the response of a zinc-carbon battery,
the voltage dropping sharply initially and then recovering. Curves B and C are typical of the response
of a zinc/alkaline/manganese dioxide battery, the voltage initially falling and either maintaining the
lower voltage or dropping slowly as the pulse discharge continues.
The type of response shown in Fig. 3.15a is also typical of batteries that have developed a pro-
tective or passivating film on an electrode, the voltage recovering as the film is broken during the
discharge (see Sec. 3.2.12 on voltage delay). The specific characteristics, however, are dependent