Page 316 - MATLAB an introduction with applications
P. 316
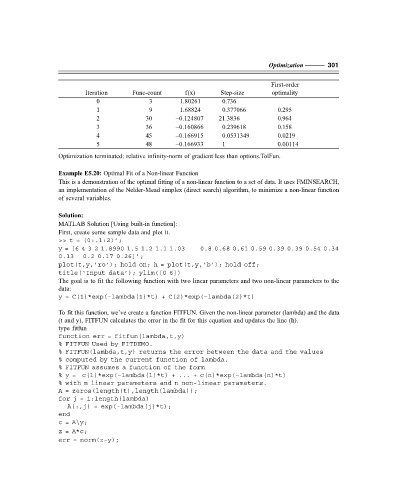
Optimization ——— 301
First-order
Iteration Func-count f(x) Step-size optimality
0 3 1.80261 0.736
1 9 1.68824 0.377066 0.295
2 30 –0.124807 21.3836 0.964
3 36 –0.160866 0.239618 0.158
4 45 –0.166915 0.0531349 0.0219
5 48 –0.166933 1 0.00114
Optimization terminated: relative infinity-norm of gradient less than options.TolFun.
Example E5.20: Optimal Fit of a Non-linear Function
This is a demonstration of the optimal fitting of a non-linear function to a set of data. It uses FMINSEARCH,
an implementation of the Nelder-Mead simplex (direct search) algorithm, to minimize a non-linear function
of several variables.
Solution:
MATLAB Solution [Using built-in function]:
First, create some sample data and plot it.
>> t = (0:.1:2)’;
y = [6 4 3 2 1.8990 1.5 1.2 1.1 1.03 0.8 0.68 0.61 0.59 0.39 0.39 0.54 0.34
0.13 0.2 0.17 0.26]’;
plot(t,y,’ro’); hold on; h = plot(t,y,‘b’); hold off;
title(‘Input data’); ylim([0 6])
The goal is to fit the following function with two linear parameters and two non-linear parameters to the
data:
y = C(1)*exp(-lambda(1)*t) + C(2)*exp(–lambda(2)*t)
To fit this function, we’ve create a function FITFUN. Given the non-linear parameter (lambda) and the data
(t and y), FITFUN calculates the error in the fit for this equation and updates the line (h).
type fitfun
function err = fitfun(lambda,t,y)
% FITFUN Used by FITDEMO.
% FITFUN(lambda,t,y) returns the error between the data and the values
% computed by the current function of lambda.
% FITFUN assumes a function of the form
% y = c(1)*exp(–lambda(1)*t) + ... + c(n)*exp(–lambda(n)*t)
% with n linear parameters and n non-linear parameters.
A = zeros(length(t),length(lambda));
for j = 1:length(lambda)
A(:,j) = exp(-lambda(j)*t);
end
c = A\y;
z = A*c;
err = norm(z–y);