Page 40 - MATLAB an introduction with applications
P. 40
MATLAB Basics ——— 25
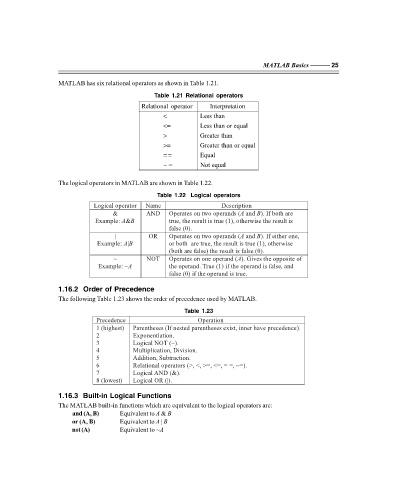
MATLAB has six relational operators as shown in Table 1.21.
Table 1.21 Relational operators
Relational operator Interpretation
< Less than
<= Less than or equal
> Greater than
>= Greater than or equal
== Equal
~ = Not equal
The logical operators in MATLAB are shown in Table 1.22.
Table 1.22 Logical operators
Logical operator Name Description
B
& AND Operates on two operands ( and ). If both are
A
Example: &AB true, the result is true (1), otherwise the result is
false (0).
| OR Operates on two operands ( and ). If either one,
B
A
Example: |AB or both are true, the result is true (1), otherwise
(both are false) the result is false (0).
~ NOT Operates on one operand ( ). Gives the opposite of
A
Example: ~A the operand. True (1) if the operand is false, and
false (0) if the operand is true.
1.16.2 Order of Precedence
The following Table 1.23 shows the order of precedence used by MATLAB.
Table 1.23
Precedence Operation
1 (highest) Parentheses (If nested parentheses exist, inner have precedence).
2 Exponentiation.
3 Logical NOT (~).
4 Multiplication, Division.
5 Addition, Subtraction.
6 Relational operators (>, <, >=, <=, = =, ~=).
7 Logical AND (&).
8 (lowest) Logical OR (|).
1.16.3 Built-in Logical Functions
The MATLAB built-in functions which are equivalent to the logical operators are:
and (A, B) Equivalent to A & B
or (A, B) Equivalent to A | B
not (A) Equivalent to ~A
F:\Final Book\Sanjay\IIIrd Printout\Dt. 10-03-09