Page 41 - MATLAB an introduction with applications
P. 41
26 ——— MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
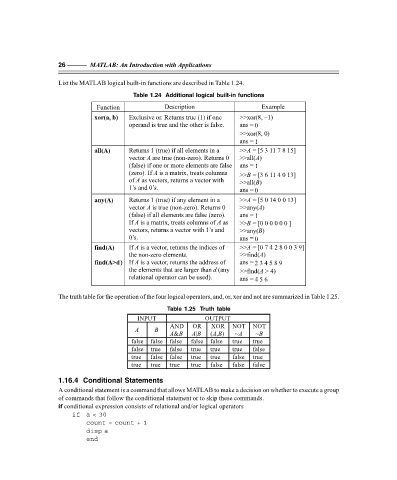
List the MATLAB logical built-in functions are described in Table 1.24.
Table 1.24 Additional logical built-in functions
Function Description Example
xor(a, b) Exclusive or. Returns true (1) if one >>xor(8, –1)
operand is true and the other is false. ans = 0
>>xor(8, 0)
ans = 1
A
all(A) Returns 1 (true) if all elements in a >> = [5 3 11 7 8 15]
A
-
vector are true (non zero). Returns 0 >>all( )
A
(false) if one or more elements are false ans = 1
(zero). If is a matrix, treats columns >> = [3 6 11 4 0 13]
A
B
of as vectors, returns a vector with >>all( )
A
B
1’s and 0’s. ans = 0
any(A) Returns 1 (true) if any element in a >> = [5 0 14 0 0 13]
A
A
-
A
vector is true (non zero). Returns 0 >>any( )
(false) if all elements are false (zero). ans = 1
A
A
If is a matrix, treats columns of as >> = [0 0 0 0 0 0 ]B
vectors, returns a vector with 1’s and >>any( )
B
0’s. ans = 0
find(A) If is a vector, returns the indices of >> = [0 7 4 2 8 0 0 3 9]
A
A
the non zero elements. >>find( )
-
A
find(A>d) If is a vector, returns the address of A ans = 2 3 4 5 8 9
the elements that are larger than (any >>find( > 4)
d
A
relational operator can be used). ans = 4 5 6
The truth table for the operation of the four logical operators, and, or, xor and not are summarized in Table 1.25.
Table 1.25 Truth table
INPUT OUTPUT
AND OR XOR NOT NOT
A B
AB& AB| (, ) ~A ~B
AB
false false false false false true true
false true false true true true false
true false false true true false true
true true true true false false false
1.16.4 Conditional Statements
A conditional statement is a command that allows MATLAB to make a decision on whether to execute a group
of commands that follow the conditional statement or to skip these commands.
if conditional expression consists of relational and/or logical operators
if a < 30
count = count + 1
disp a
end
F:\Final Book\Sanjay\IIIrd Printout\Dt. 10-03-09