Page 44 - MATLAB an introduction with applications
P. 44
MATLAB Basics ——— 29
1
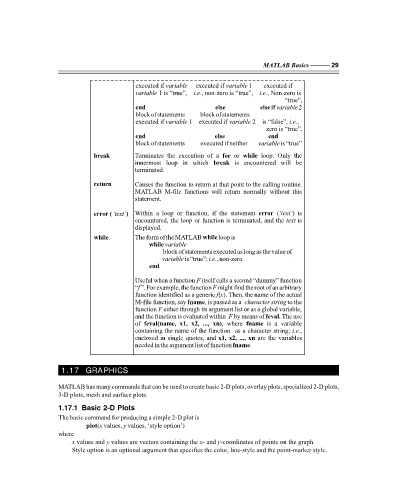
executed if variable executed if variable executed if
1 is “true”, i.e.
-
variable , non zero is “true”, i.e. , Non zero is
-
“true”,
end else else if variable 2
block of statements block of statements
executed if variable 1 executed if variable 2 is “false”, i.e. ,
zero is “true”,
end else end
block of statements executed if neither variable is “true”
break Terminates the execution of a for or while loop. Only the
innermost loop in which break is encountered will be
terminated.
return Causes the function to return at that point to the calling routine.
MATLAB M-file functions will return normally without this
statement.
error (‘text’) Within a loop or function, if the statement error (‘text ’) is
encountered, the loop or function is terminated, and the text is
displayed.
while The form of the MATLAB while loop is
while variable
block of statements executed as long as the value of
variable is “true”; i.e., non -zero
end
Useful when a function F itself calls a second “dummy” function
f “ ”. For example, the function F might find the root of an arbitrary
function identified as a generic fx). Then, the name of the actual
(
M-file function, say fname , is passed as a character string to the
function F either through its argument list or as a global variable,
and the function is evaluated within F by means of feval. The use
of feval(name, x1, x2, ..., xn) , where fname is a variable
containing the name of the function as a character string; i.e.,
enclosed in single quotes, and x1, x2, ..., xn are the variables
needed in the argument list of function fname .
1.17 GRAPHICS
MATLAB has many commands that can be used to create basic 2-D plots, overlay plots, specialized 2-D plots,
3-D plots, mesh and surface plots.
1.17.1 Basic 2-D Plots
The basic command for producing a simple 2-D plot is
plot(x values, y values, ‘style option’)
where
x values and y values are vectors containing the x- and y-coordinates of points on the graph.
Style option is an optional argument that specifies the color, line-style and the point-marker style.
F:\Final Book\Sanjay\IIIrd Printout\Dt. 10-03-09