Page 217 - MATLAB Recipes for Earth Sciences
P. 217
9 Multivariate Statistics
9.1 Introduction
Multivariate analysis aims to understand and describe the relationship be-
tween an arbitrary number of variables. Earth scientists often deal with
multivariate data sets, such as microfossil assemblages, geochemical finger-
prints of volcanic ashes or clay mineral contents of sedimentary sequences.
If there are complex relationships between the different parameters, univari-
ate statistics ignores the information content of the data. There are number
of methods for investigating the scaling properties of multivariate data.
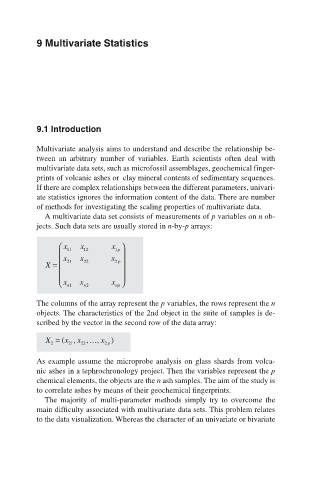
A multivariate data set consists of measurements of p variables on n ob-
jects. Such data sets are usually stored in n-by-p arrays:
The columns of the array represent the p variables, the rows represent the n
objects. The characteristics of the 2nd object in the suite of samples is de-
scribed by the vector in the second row of the data array:
As example assume the microprobe analysis on glass shards from volca-
nic ashes in a tephrochronology project. Then the variables represent the p
chemical elements, the objects are the n ash samples. The aim of the study is
to correlate ashes by means of their geochemical fi ngerprints.
The majority of multi-parameter methods simply try to overcome the
main difficulty associated with multivariate data sets. This problem relates
to the data visualization. Whereas the character of an univariate or bivariate