Page 143 - Machine Learning for Subsurface Characterization
P. 143
Stacked neural network architecture Chapter 4 119
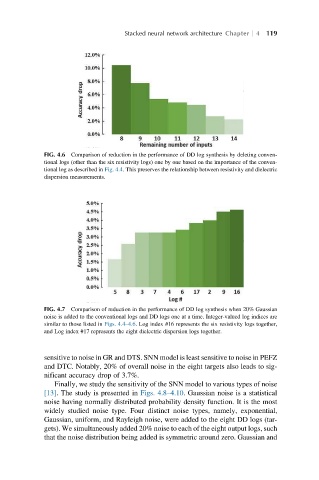
FIG. 4.6 Comparison of reduction in the performance of DD log synthesis by deleting conven-
tional logs (other than the six resistivity logs) one by one based on the importance of the conven-
tional log as described in Fig. 4.4. This preserves the relationship between resistivity and dielectric
dispersion measurements.
FIG. 4.7 Comparison of reduction in the performance of DD log synthesis when 20% Gaussian
noise is added to the conventional logs and DD logs one at a time. Integer-valued log indices are
similar to those listed in Figs. 4.4–4.6. Log index #16 represents the six resistivity logs together,
and Log index #17 represents the eight dielectric dispersion logs together.
sensitive to noise in GR and DTS. SNN model is least sensitive to noise in PEFZ
and DTC. Notably, 20% of overall noise in the eight targets also leads to sig-
nificant accuracy drop of 3.7%.
Finally, we study the sensitivity of the SNN model to various types of noise
[13]. The study is presented in Figs. 4.8–4.10. Gaussian noise is a statistical
noise having normally distributed probability density function. It is the most
widely studied noise type. Four distinct noise types, namely, exponential,
Gaussian, uniform, and Rayleigh noise, were added to the eight DD logs (tar-
gets). We simultaneously added 20% noise to each of the eight output logs, such
that the noise distribution being added is symmetric around zero. Gaussian and