Page 163 - Macromolecular Crystallography
P. 163
152 MACROMOLECULAR CRYS TALLOGRAPHY
(a) (b)
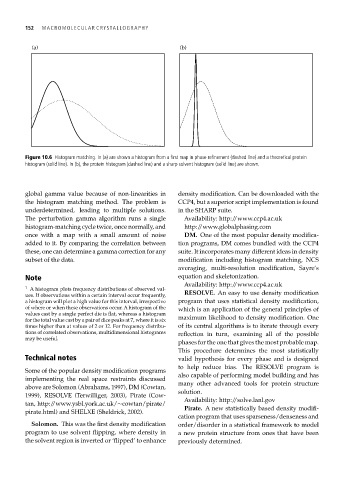
Figure 10.6 Histogram matching. In (a) are shown a histogram from a first map in phase refinement (dashed line) and a theoretical protein
histogram (solid line). In (b), the protein histogram (dashed line) and a sharp solvent histogram (solid line) are shown.
global gamma value because of non-linearities in density modification. Can be downloaded with the
the histogram matching method. The problem is CCP4, but a superior script implementation is found
underdetermined, leading to multiple solutions. in the SHARP suite.
The perturbation gamma algorithm runs a single Availability: http://www.ccp4.ac.uk
histogram-matching cycle twice, once normally, and http://www.globalphasing.com
once with a map with a small amount of noise DM. One of the most popular density modifica-
added to it. By comparing the correlation between tion programs, DM comes bundled with the CCP4
these, one can determine a gamma correction for any suite. It incorporates many different ideas in density
subset of the data. modification including histogram matching, NCS
averaging, multi-resolution modification, Sayre’s
Note equation and skeletonization.
Availability: http://www.ccp4.ac.uk
1
A histogram plots frequency distributions of observed val-
ues. If observations within a certain interval occur frequently, RESOLVE. An easy to use density modification
a histogram will plot a high value for this interval, irrespective program that uses statistical density modification,
of where or when these observations occur. A histogram of the which is an application of the general principles of
values cast by a single perfect die is flat, whereas a histogram
for the total value cast by a pair of dice peaks at 7, where it is six maximum likelihood to density modification. One
times higher than at values of 2 or 12. For frequency distribu- of its central algorithms is to iterate through every
tions of correlated observations, multidimensional histograms reflection in turn, examining all of the possible
may be useful.
phases for the one that gives the most probable map.
This procedure determines the most statistically
Technical notes valid hypothesis for every phase and is designed
to help reduce bias. The RESOLVE program is
Some of the popular density modification programs
also capable of performing model building and has
implementing the real space restraints discussed
many other advanced tools for protein structure
above are Solomon (Abrahams, 1997), DM (Cowtan,
solution.
1999), RESOLVE (Terwilliger, 2003), Pirate (Cow-
Availability: http://solve.lanl.gov
tan, http://www.ysbl.york.ac.uk/∼cowtan/pirate/
Pirate. A new statistically based density modifi-
pirate.html) and SHELXE (Sheldrick, 2002).
cation program that uses sparseness/denseness and
Solomon. This was the first density modification order/disorder in a statistical framework to model
program to use solvent flipping, where density in a new protein structure from ones that have been
the solvent region is inverted or ‘flipped’ to enhance previously determined.